Mass spectrometry techniques in the survey of steroid metabolites as potential disease biomarkers: a review
- PMID: 23664145
- PMCID: PMC3755027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.04.003
Mass spectrometry techniques in the survey of steroid metabolites as potential disease biomarkers: a review
Abstract
Mass spectrometric approaches have been fundamental to the identification of metabolites associated with steroid hormones, yet this topic has not been reviewed in depth in recent years. To this end, and given the increasing relevance of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) studies on steroid hormones and their metabolites, the present review addresses this subject. This review provides a timely summary of the use of various mass spectrometry-based analytical techniques during the evaluation of steroidal biomarkers in a range of human disease settings. The sensitivity and specificity of these technologies are clearly providing valuable new insights into breast cancer and cardiovascular disease. We aim to contribute to an enhanced understanding of steroid metabolism and how it can be profiled by LC-MS techniques.
Keywords: 1,2-Dihydroxybenzene (benzene catechol); 1,2-Dihydroxybenzene-Quinone; APCI–MS; APPI–MS; Atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry; Atmospheric-pressure photoionization mass spectrometry; CA; CAT; CAT-Q; CID; COMT; Cancer biomarkers; Catechol-O-methyltransferase; Cholesterol metabolites; Cholic acid; Collision-induced dissociation; DCA; Deoxycholic acid; ESI–MS; Electrospray ionization; Estradiol metabolites; FIA; FTMS; Flow injection analysis; Fourier transform mass spectrometry; GC–MS; GP; Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry; Girard P; HPLC–EDC; High performance liquid chromatography–electro-chemical detection; LC–MS; Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; MALDI-TOF; Mass spectrometry; Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight; N-AcCys; N-acetylcysteine; N-acetyldopamine; N-acetyldopamine-quinone; NADA; NADA-Q; NQO-2; NRH quinone oxidoreductase 2; Resv; Resveratrol; SLOS; SPE; SRM; Selected reaction monitoring; Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome; Solid phase extration; TOF; Time-of-flight; UPLC–MS/MS; Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Crown Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

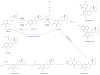
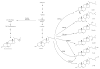
References
-
- Want EJ, Cravatt BF, Siuzdak G. The expanding role of mass spectrometry in metabolite profiling and characterization. ChemBioChem. 2005;6:1941–51. - PubMed
-
- Dear GJ, Plumb AR, Fraser IJ. The rapid identification of drug metabolites using capillary liquid chromatography coupled to an ion trap mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1999;3:456–63. - PubMed
-
- Zhang N, Fountain ST, Bi H, Rossi ST. Quantification and rapid metabolite identification in drug discovery using API Time-of-Flight LC/MS. Anal Chem. 2000;72:800–6. - PubMed
-
- Shockor JP, Holmes E. Metabonomic Applications in Toxicity Screening and Disease Diagnosis. Current Trop Med Chem. 2002;2:35–51. - PubMed
-
- Plumb RS, Stumpf CL, Granger JH, Castro-Perez J, Haselden JN, Dear GJ. Use of liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis shows promise for the detection of drug metabolites in biological fluids. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17:2632–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

