Neurotransmitter transporters: structure meets function
- PMID: 23664361
- PMCID: PMC3654398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2013.03.002
Neurotransmitter transporters: structure meets function
Abstract
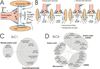
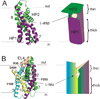
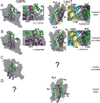
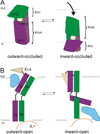
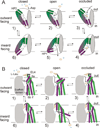
At synapses, sodium-coupled transporters remove released neurotransmitters, thereby recycling them and maintaining a low extracellular concentration of the neurotransmitter. The molecular mechanism underlying sodium-coupled neurotransmitter uptake is not completely understood. Several structures of homologs of human neurotransmitter transporters have been solved with X-ray crystallography. These crystal structures have spurred a plethora of computational and experimental work to elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying sodium-coupled transport. Here, we compare the structures of GltPh, a glutamate transporter homolog, and LeuT, a homolog of neurotransmitter transporters for the biogenic amines and inhibitory molecules GABA and glycine. We relate these structures to data obtained from experiments and computational simulations, to draw conclusions about the mechanism of uptake by sodium-coupled neurotransmitter transporters. Here, we propose how sodium and substrate binding is coupled and how binding of sodium and substrate opens and closes the gates in these transporters, thereby leading to an efficient coupled transport.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bendahan A, Armon A, Madani N, Kavanaugh MP, Kanner BI. Arginine 447 plays a pivotal role in substrate interactions in a neuronal glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:37436–37442. - PubMed
-
- Billups B, Rossi D, Oshima T, Warr O, Takahashi M, Sarantis M, Szatkowski M, Attwell D. Physiological and pathological operation of glutamate transporters. Prog Brain Res. 1998;116:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Boudker O, Ryan RM, Yernool D, Shimamoto K, Gouaux E. Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter. Nature. 2007;445:387–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

