Regulation of lung injury and fibrosis by p53-mediated changes in urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PMID: 23665346
- PMCID: PMC3702744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.03.022
Regulation of lung injury and fibrosis by p53-mediated changes in urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
Abstract
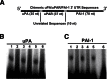
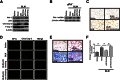
Alveolar type II epithelial cell (ATII) apoptosis and proliferation of mesenchymal cells are the hallmarks of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a devastating disease of unknown cause characterized by alveolar epithelial injury and progressive fibrosis. We used a mouse model of bleomycin (BLM)-induced lung injury to understand the involvement of p53-mediated changes in urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels in the regulation of alveolar epithelial injury. We found marked induction of p53 in ATII cells from mice exposed to BLM. Transgenic mice expressing transcriptionally inactive dominant negative p53 in ATII cells showed augmented apoptosis, whereas those deficient in p53 resisted BLM-induced ATII cell apoptosis. Inhibition of p53 transcription failed to suppress PAI-1 or induce uPA mRNA in BLM-treated ATII cells. ATII cells from mice with BLM injury showed augmented binding of p53 to uPA, uPA receptor (uPAR), and PAI-1 mRNA. p53-binding sequences from uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 mRNA 3' untranslated regions neither interfered with p53 DNA binding activity nor p53-mediated promoter transactivation. However, increased expression of p53-binding sequences from uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 mRNA 3' untranslated regions in ATII cells suppressed PAI-1 and induced uPA after BLM treatment, leading to inhibition of ATII cell apoptosis and pulmonary fibrosis. Our findings indicate that disruption of p53-fibrinolytic system cross talk may serve as a novel intervention strategy to prevent lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Bhandary Y.P., Shetty S.K., Marudamuthu A.S., Gyetko M.R., Idell S., Gharaee-Kermani M., Shetty R.S., Starcher B.C., Shetty S. Regulation of alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis and pulmonary fibrosis by coordinate expression of components of the fibrinolytic system. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302:L463–L473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shetty S.K., Bhandary Y.P., Marudamuthu A.S., Abernathy D., Velusamy T., Starcher B., Shetty S. Regulation of airway and alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis by p53 induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 during cigarette smoke exposure injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012;47:474–483. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

