Comparison of behavioral effects of the NMDA receptor channel blockers memantine and ketamine in rats
- PMID: 23665480
- PMCID: PMC3723459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.05.005
Comparison of behavioral effects of the NMDA receptor channel blockers memantine and ketamine in rats
Abstract
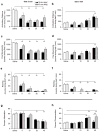
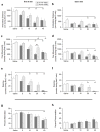
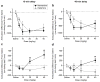
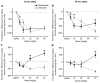
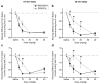
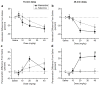
Memantine and ketamine block N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors with similar affinity and kinetics, yet their behavioral consequences differ: e.g., memantine is used to alleviate symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, whereas ketamine reproduces symptoms of schizophrenia. The two drugs exhibit different pharmacokinetics, which may play a principal role in their differential behavioral effects. To gain insight into the drugs' behavioral consequences, we treated adult male rats acutely with varying doses (0-40 mg/kg i.p.) of memantine or ketamine and assessed exploratory behavior and spatial working memory. To examine the importance of pharmacokinetics, we assessed behavior either 15 or 45 min after drug administration. Both drugs decreased ambulation, fine movements, and rearing at the beginning of the exploratory activity test; however, at the end of the test, high doses of only memantine increased ambulation and fine movements. High doses of both drugs disrupted spontaneous alternation, a measure of working memory, but high doses of only memantine elicited perseverative behavior. Surprisingly, ketamine's effects were influenced by the delay between drug administration and testing no more frequently than were memantine's. Our findings show that, regardless of test delay, memantine and ketamine evoke similar behavioral effects at lower doses, consistent with NMDA receptors being both drugs' principal site of action, but can have divergent effects at higher doses. Our results suggest that the divergence of memantine's and ketamine's behavioral consequences is likely to result from differences in mechanisms of NMDA receptor antagonism or actions at other targets.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no actual or potential conflict of interest with the information reported here.
Figures
References
-
- Alessandri B, Battig K, Welzl H. Effects of ketamine on tunnel maze and water maze performance in the rat. Behav Neural Biol. 1989;52:194–212. - PubMed
-
- Aracava Y, Pereira EF, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Memantine blocks alpha7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors more potently than N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat hippocampal neurons.[see comment] Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics. 2005;312:1195–205. - PubMed
-
- Blanpied TA, Boeckman FA, Aizenman E, Johnson JW. Trapping channel block of NMDA-activated responses by amantadine and memantine. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:309–23. - PubMed
-
- Chen HSV, Lipton SA. Pharmacological implications of two distinct mechanisms of interaction of memantine with N-methyl-D-aspartate-gated channels. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2005;314:961–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

