ProP is required for the survival of desiccated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium cells on a stainless steel surface
- PMID: 23666329
- PMCID: PMC3697505
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00515-13
ProP is required for the survival of desiccated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium cells on a stainless steel surface
Abstract
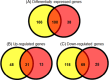
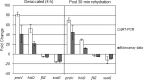
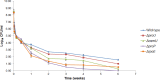
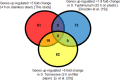
Consumers trust commercial food production to be safe, and it is important to strive to improve food safety at every level. Several outbreaks of food-borne disease have been caused by Salmonella strains associated with dried food. Currently we do not know the mechanisms used by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to survive in desiccated environments. The aim of this study was to discover the responses of S. Typhimurium ST4/74 at the transcriptional level to desiccation on a stainless steel surface and to subsequent rehydration. Bacterial cells were dried onto the same steel surfaces used during the production of dry foods, and RNA was recovered for transcriptomic analysis. Subsequently, dried cells were rehydrated and were again used for transcriptomic analysis. A total of 266 genes were differentially expressed under desiccation stress compared with a static broth culture. The osmoprotectant transporters proP, proU, and osmU (STM1491 to STM1494) were highly upregulated by drying. Deletion of any one of these transport systems resulted in a reduction in the long-term viability of S. Typhimurium on a stainless steel food contact surface. The proP gene was critical for survival; proP deletion mutants could not survive desiccation for long periods and were undetectable after 4 weeks. Following rehydration, 138 genes were differentially expressed, with upregulation observed for genes such as proP, proU, and the phosphate transport genes (pstACS). In time, this knowledge should prove valuable for understanding the underlying mechanisms involved in pathogen survival and should lead to improved methods for control to ensure the safety of intermediate- and low-moisture foods.
Figures
References
-
- Podolak R, Enache E, Stone W, Black DG, Elliott PH. 2010. Sources and risk factors for contamination, survival, persistence, and heat resistance of Salmonella in low-moisture foods. J. Food Prot. 73:1919–1936 - PubMed
-
- Kotzekidou P. 1998. Microbial stability and fate of Salmonella Enteritidis in halva, a low-moisture confection. J. Food Prot. 61:181–185 - PubMed
-
- Nummer B, Smith J. 2012. Survival of Salmonella in a high sugar, low water-activity, peanut butter flavored candy fondant. Food Control 27:184–187
-
- Gruzdev N, Pinto R. 2012. Persistence of Salmonella enterica during dehydration and subsequent cold storage. Food Microbiol. 32:415–422 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

