Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on phosphorylated protein signaling in children undergoing tetralogy of Fallot repair: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23666460
- PMCID: PMC3698768
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000095
Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on phosphorylated protein signaling in children undergoing tetralogy of Fallot repair: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Our previous randomized controlled trial demonstrated cardiorespiratory protection by remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) in children before cardiac surgery. However, the impact of RIPC on myocardial prosurvival intracellular signaling remains unknown in cyanosis. RIPC may augment phosphorylated protein signaling in myocardium and circulating leukocytes during tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) repair.
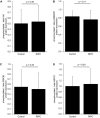
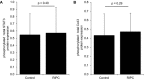
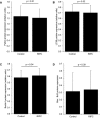
Methods and results: Children (n=40) undergoing ToF repair were double-blind randomized to RIPC (n=11 boys, 9 girls) or control (sham RIPC: n=9 boys, 11 girls). Blood samples were taken before, immediately after, and 24 hours after cardiopulmonary bypass. Resected right ventricular outflow tract muscle and leukocytes were processed for protein expression and mitochondrial respiration. There was no difference in age (7.1 ± 3.4 versus 7.1 ± 3.4 months), weight (7.7 ± 1.8 versus 7.5 ± 1.9 kg), or bypass or aortic cross-clamp times between the groups (control versus RIPC, mean±SD). No differences were seen between the groups for an increase in the ratio of phosphorylated to total protein for protein kinase B, p38 mitogen activated protein kinase, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, glycogen synthase kinase 3β, heat shock protein 27, Connexin43, or markers associated with promotion of necrosis (serum cardiac troponin I), apoptosis (Bax, Bcl-2), and autophagy (Parkin, Beclin-1, LC3B). A high proportion of total proteins were in phosphorylated form in control and RIPC myocardium. In leukocytes, mitochondrial respiration and assessed protein levels did not differ between groups.
Conclusions: In patients with cyanotic heart disease, a high proportion of proteins are in phosphorylated form. RIPC does not further enhance phosphorylated protein signaling in myocardium or circulating leukocytes in children undergoing ToF repair.
Clinical trial registration: URL: (http://www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?id=335613. Unique identifier: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry number ACTRN12610000496011.
Keywords: cyanosis; heart; mitochondria; pediatric surgery; remote ischemic preconditioning; tetralogy of Fallot.
Figures
References
-
- Kharbanda RK, Mortensen UM, White PA, Kristiansen SB, Schmidt MR, Hoschtitzky JA, Vogel M, Sorensen K, Redington AN, MacAllister R. Transient limb ischemia induces remote ischemic preconditioning in vivo. Circulation. 2002; 106:2881-2883 - PubMed
-
- Cheung MM, Kharbanda RK, Konstantinov IE, Shimizu M, Frndova H, Li J, Holtby HM, Cox PN, Smallhorn JF, Van Arsdell GS, Redington AN. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on children undergoing cardiac surgery: first clinical application in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 47:2277-2282 - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Mwamure PK, Venugopal V, Harris J, Barnard M, Grundy E, Ashley E, Vichare S, Di Salvo C, Kolvekar S, Hayward M, Keogh B, MacAllister RJ, Yellon DM. Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on myocardial injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007; 370:575-579 - PubMed
-
- Ali ZA, Callaghan CJ, Lim E, Ali AA, Nouraei SA, Akthar AM, Boyle JR, Varty K, Kharbanda RK, Dutka DP, Gaunt ME. Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces myocardial and renal injury after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2007; 116:198-205 - PubMed
-
- Li J, Xuan W, Yan R, Tropak MB, Jean‐St‐Michel E, Liang W, Gladstone R, Backx PH, Kharbanda RK, Redington AN. Remote preconditioning provides potent cardioprotection via PI3K/AKT activation and is associated with nuclear accumulation of beta‐catenin. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011; 120:451-462 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

