Impact of major non-cardiac complications on outcome following cardiac surgery procedures: logistic regression analysis in a very recent patient cohort
- PMID: 23667066
- PMCID: PMC3715168
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivt149
Impact of major non-cardiac complications on outcome following cardiac surgery procedures: logistic regression analysis in a very recent patient cohort
Abstract
Objectives: In this study, we sought to analyse the incidence of major non-cardiac complications and their impact on survival following cardiac surgery procedures in a contemporary patient cohort. We further determined independent predictors of perioperative mortality and created a logistic regression model for prediction of outcome after the occurrence of these complications.
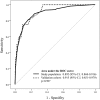
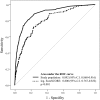
Methods: Prospectively collected data of 5318 consecutive adult patients (mean age 68.9±11.0 years; 29.3% [n=1559] female) undergoing cardiac surgery from January 2009 to May 2012 were retrospectively analysed. Outcome measures were six major non-cardiac complications including respiratory failure, dialysis-dependent renal failure, deep sternal wound infection (DSWI), cerebrovascular accident (CVA), gastrointestinal complications (GIC) and sepsis and their impact on perioperative mortality and hospital length of stay using multivariate regression models. The discriminatory power was evaluated by calculating the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (C statistic).
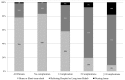
Results: A total of 1321 complications were observed in 846 (15.9%) patients: respiratory failure (n=432; 8.1%), dialysis-dependent renal failure (n=295; 5.5%), GIC (n=154; 2.9%), CVA (n=151; 2.8%), DSWI (n=146; 2.7%) and sepsis (n=143; 2.7%). Perioperative mortality was 17.0% in patients with at least one major non-cardiac complication and correlated with the number of complications (single, 9.7%; n=53/549; double, 24.0%; n=44/183; ≥3, 41.2%; n=47/114, P<0.001). Six preoperative and four postoperative independent predictors of operative mortality were identified (age (odds ratio [OR] 1.8; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.3-2.4), peripheral vascular disease (OR 2.6; 95% CI 1.6-4.2), pulmonary hypertension (OR 2.7; 95% CI 1.5-4.9), atrial fibrillation (OR 1.5; 95% CI 1.0-2.3), emergency (OR 5.0; 95% CI 3.4-7.2), other procedures than CABG (OR 1.5; 95% CI 1.0-2.1), postoperative dialysis (OR 4.0; 95% CI 2.6-6.1), sepsis (OR 3.4; 95% CI 2.0-5.6), respiratory failure (OR 3.2; 95% CI 2.2-4.9), GIC (OR 3.2; 95% CI 1.9-5.3)) and included in the logistic model, which accurately predicted outcome (C statistic, 0.892; 95% CI 0.868-0.916). Length of hospital stay was significantly increased according to the number of complications (single: median 15 (IQR 10-24) days, double: 16 (IQR 8-28) days, ≥3: 20 (IQR 13-39) days, P<0.001).
Conclusions: With a worsening in the risk profile of patients undergoing cardiac surgery, an increasing number of patients develop major complications leading to increased length of stay and mortality, which is correlated to the number and severity of these complications. Our predictive model based on preoperative and postoperative variables allowed us to determine with accuracy the perioperative mortality in critically ill patients after cardiac surgery.
Keywords: Cardiac surgery; Mortality; Outcome; Postoperative complications.
Figures
References
-
- ElBardissi AW, Aranki SF, Sheng S, O'Brien SM, Greenberg CC, Gammie JS. Trends in isolated coronary artery bypass grafting: an analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons adult cardiac surgery database. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;143:273–81. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SM, Shahian DM, Filardo G, Ferraris VA, Haan CK, Rich JB, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2008 cardiac surgery risk models: part 2—isolated valve surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:S23–42. - PubMed
-
- Rahmanian PB, Adams DH, Castillo JG, Carpentier A, Filsoufi F. Predicting hospital mortality and analysis of long-term survival after major noncardiac complications in cardiac surgery patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90:1221–9. - PubMed
-
- Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S. Applied logistic regression. New York: Wiley; 1989.
-
- Lemeshow S, Le Gall JR. Modeling the severity of illness of ICU patients. A systems update. JAMA. 1994;272:1049–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

