Evaluation of multimodal imaging in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 23669302
- PMCID: PMC3974115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.05.003
Evaluation of multimodal imaging in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
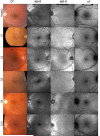
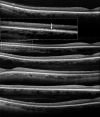
The aim of this study was to investigate visualization of the tapetal-like reflex using current imaging modalities and evaluate SD-OCT changes in known carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP); the objective being the development of an optimal protocol for clinicians to identify carriers. Ten XLRP carriers (19 eyes) were examined using color fundus photography, 488 nm reflectance (488-R), near-infrared reflectance (NIR-R), autofluorescence (AF) and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) imaging (Spectralis SLO-OCT, Heidelberg). Horizontal line scans through the fovea were acquired in all subjects and in a group of 10 age-similar controls. Peripheral SD-OCT scans (extending to 27.5° eccentricity) were also acquired in both eyes of 7 carriers. MP-1 microperimetery (10-2 pattern; Nidek) was performed in one eye of each carrier. For the XLRP carriers, a tapetal reflex was observed with all imaging modalities in 8 of 19 eyes. It had the same retinal location on color fundus, 488-R and NIR-R imaging but a different location on AF. The tapetal reflex was most easily detected in 488-R images. The horizontal foveal SD-OCT scans were qualitatively normal, but measurements showed significant outer retinal layer thinning in all eyes. Additionally, the 14 eyes with peripheral SD-OCTs demonstrated patchy loss of the inner segment ellipsoid band. Microperimetry exhibited patchy visual sensitivity loss in 9 eyes. Full field ERGs were variable, ranging from normal to severely abnormal rod and cone responses. Our findings suggest that an optimal protocol for identifying carriers of XLRP should include 488-R imaging in a multimodal approach. Peripheral SD-OCT imaging and central retinal layer quantification revealed significant structural abnormalities.
Keywords: X-linked retinitis pigmentosa; microperimetry; scanning laser ophthalmoscope; spectral domain optical coherence tomograph; tapetal-like reflex.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Alexander KR, Barnes CS, Fishman GA. ON-pathway dysfunction and timing properties of the flicker ERG in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:4017–4025. - PubMed
-
- Andreasson S, Breuer DK, Eksandh L, Ponjavic V, Frennesson C, Hiriyanna S, Filippova E, Yashar BM, Swaroop A. Clinical studies of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa in three Swedish families with newly identified mutations in the RP2 and RPGR-ORF15 genes. Ophthalmic Genet. 2003;24:215–223. - PubMed
-
- Banin E, Mizrahi-Meissonnier L, Neis R, Silverstein S, Magyar I, Abeliovich D, Roepman R, Berger W, Rosenberg T, Sharon D. A non-ancestral RPGR missense mutation in families with either recessive or semi-dominant X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A:1150–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

