Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde
- PMID: 23670533
- PMCID: PMC3707160
- DOI: 10.3390/md11051534
Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde
Abstract
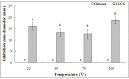
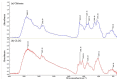
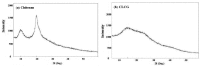
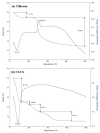
This present study deals with synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde. Results from this study indicated that cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde markedly inhibited the growth of antibiotic-resistant Burkholderia cepacia complex regardless of bacterial species and incubation time while bacterial growth was unaffected by solid chitosan. Furthermore, high temperature treated cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde showed strong antibacterial activity against the selected strain 0901 although the inhibitory effects varied with different temperatures. In addition, physical-chemical and structural characterization revealed that the cross-linking of chitosan with glutaraldehyde resulted in a rougher surface morphology, a characteristic Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) band at 1559 cm⁻¹, a specific X-ray diffraction peak centered at 2θ = 15°, a lower contents of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, and a higher stability of glucose units compared to chitosan based on scanning electron microscopic observation, FTIR spectra, X-ray diffraction pattern, as well as elemental and thermo gravimetric analysis. Overall, this study indicated that cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde is promising to be developed as a new antibacterial drug.
Figures

References
-
- Vanlaere E., Lipuma J.J., Baldwin A., Henry D., De Brandt E., Mahenthiralingam E., Speert D., Dowson C., Vandamme P. Burkholderia latens sp. nov., Burkholderia diffusa sp. nov., Burkholderia arboris sp. nov., Burkholderia seminalis sp. nov. and Burkholderia metallica sp. nov., novel species within the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008;58:1580–1590. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65634-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vanlaere E., Baldwin A., Gevers D., Henry D., Brandt E.D., LiPuma J.J. Taxon K, a complex within the Burkholderia cepacia complex, comprises at least two novel species: Burkholderia contaminans sp. nov. and Burkholderia lata sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009;59:102–111. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.001123-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fang Y., Lou M.M., Li B., Xie G.L., Wang F., Zhang L.X., Luo Y.C. Characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex from cystic fibrosis patients in China and their chitosan susceptibility. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010;26:443–450. doi: 10.1007/s11274-009-0187-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

