Spasmolytic effect of caulerpine involves blockade of Ca²⁺ influx on guinea pig ileum
- PMID: 23670534
- PMCID: PMC3707161
- DOI: 10.3390/md11051553
Spasmolytic effect of caulerpine involves blockade of Ca²⁺ influx on guinea pig ileum
Abstract
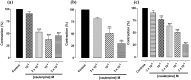
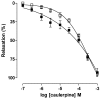
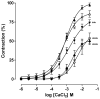
In this work, we investigated the spasmolytic effect of caulerpine, a bisindole alkaloid isolated from marine algae of the Caulerpa genus, on guinea pig ileum. Our findings indicated that caulerpine inhibited phasic contractions induced by carbachol (IC₅₀ = 7.0 ± 1.9 × 10⁻⁵ M), histamine (IC₅₀ = 1.3 ± 0.3 × 10⁻⁴ M) and serotonin (IC₅₀ = 8.0 ± 1.4 × 10⁻⁵ M) in a non-selective manner. Furthermore, caulerpine concentration-dependently inhibited serotonin-induced cumulative contractions (pD'₂ = 4.48 ± 0.08), shifting the curves to the right with Emax reduction and slope of 2.44 ± 0.21, suggesting a noncompetitive antagonism pseudo-irreversible. The alkaloid also relaxed the ileum pre-contracted by KCl (EC₅₀ = 9.0 ± 0.9 × 10⁻⁵ M) and carbachol (EC₅₀ = 4.6 ± 0.7 × 10⁻⁵ M) in a concentration-dependent manner. This effect was probably due to inhibition of Ca²⁺ influx through voltage-gated calcium channels (CaV), since caulerpine slightly inhibited the CaCl₂-induced contractions in depolarizing medium without Ca²⁺, shifting the curves to the right and with Emax reduction. According to these results, the spasmolytic effect of caulerpine on guinea pig ileum seems to involve inhibition of Ca²⁺ influx through CaV. However, other mechanisms are not discarded.
Figures


References
-
- Molinski T.F., Dalisay D.S., Lievens S.L., Saludes J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009;81:69–85. - PubMed
-
- Lira N.S., Montes R.C., Tavares J.F., da Silva M.S., da Cunha E.V., de Athayde-Filho P.F., Rodrigues L.C., da Silva Dias C., Barbosa-Filho J.M. Brominated compounds from marine sponges of the genus Aplysina and a compilation of their 13C NMR spectral data. Mar. Drugs. 2011;9:2316–2368. doi: 10.3390/md9112316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

