Surgical technique: Tscherne-Johnson extensile approach for tibial plateau fractures
- PMID: 23670670
- PMCID: PMC3734402
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-2962-2
Surgical technique: Tscherne-Johnson extensile approach for tibial plateau fractures
Abstract
Background: The standard approach to lateral tibial plateau fractures involves elevation of the iliotibial band (IT) and anterior tibialis origin in continuity from Gerdy's tubercle and metaphyseal flare. We describe an alternative approach to increase lateral plateau joint exposure and maintain iliotibial band insertion to Gerdy's tubercle.
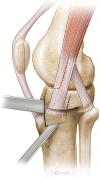
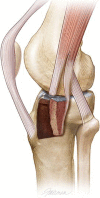
Description of technique: The approach entails a partial tenotomy of the anterior half of the IT band leaving the posterior IT band insertion attached to Gerdy's tubercle. Fracture lines around Gerdy's tubercle are completed or the tubercle was osteotomized and externally rotated and the joint overdistracted, allowing direct visualization of the joint depression. Joint elevation, grafting, and internal fixation are performed through this window.
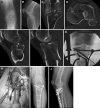
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 76 patients (two groups), Schatzker Types I to II and IV to VI fractures (66 patients), between 1989 and 2005, and 10 patients, with 10 bicondylar posterior plateau fractures, from 2002 to 2010. All patients were followed a minimum of 12 months (average, 3.9 years; range, 12 months to 10 years). Ten patients, with posterior plateau fractures, received anterolateral plateau intraarticular osteotomy for exposure of centroposterior and posterolateral articular depression.
Results: Average knee ROM was 2° of flexion (range, -3° to 5°) to greater than 120° of flexion (range, 100°-145°). In 66 patients, average articular depression improved from 7.4 mm to 1 mm (range, 0-5 mm) and, in 10 posterior fractures, from 18 mm to 1 mm (range, 0-4.5 mm). Infection occurred in one of the 76 patients; acute débridement and intravenous antibiotics resulted in control of the infection.
Conclusions: This approach reliably increases direct visualization of the lateral plateau articular fractures and maintains IT band insertion. Articular osteotomy of the anterolateral plateau provides access to extensive posterior plateau fractures.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter to the editor: Surgical technique: Tscherne-Johnson extensile approach for tibial plateau fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Dec;472(12):4035-6. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3916-z. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 25183222 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to the letter to the editor: Surgical technique: Tscherne-Johnson extensile approach for tibial plateau fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Dec;472(12):4037-8. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3917-y. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 25262336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter to the Editor: Surgical Technique: Tscherne-Johnson Extensile Approach for Tibial Plateau Fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Mar;474(3):854-6. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4653-7. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26626926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to the Letter to the Editor: Surgical Technique: Tscherne-Johnson Extensile Approach for Tibial Plateau Fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Mar;474(3):857-60. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4654-6. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26683035 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bendayan J, Noblin JD, Freeland AE. Posteromedial second incision to reduce and stabilize a displaced posterior fragment that can occur in Schatzker Type V bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Orthopedics. 1996;19:903–904. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya T, McCarty LP, III, Harris MB, Morrison S, Wixted JJ, Vrahas MS, Smith RM. The posterior shearing tibial plateau fracture: treatment and results via a posterior approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;9:305–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

