How does antiretroviral treatment attenuate the stigma of HIV? Evidence from a cohort study in rural Uganda
- PMID: 23670710
- PMCID: PMC3773278
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-013-0503-3
How does antiretroviral treatment attenuate the stigma of HIV? Evidence from a cohort study in rural Uganda
Abstract
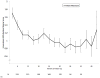
Program implementers and qualitative researchers have described how increasing availability of HIV antiretroviral therapy (ART) is associated with improvements in psychosocial health and internalized stigma. To determine whether, and through what channels, ART reduces internalized stigma, we analyzed data from 262 HIV-infected, treatment-naïve persons in rural Uganda followed from ART initiation over a median of 3.4 years. We fitted Poisson regression models with cluster-correlated robust estimates of variance, specifying internalized stigma as the dependent variable, adjusting for time on treatment as well as socio-demographic, clinical, and psychosocial variables. Over time on treatment, internalized stigma declined steadily, with the largest decline observed during the first 2 years of treatment. This trend remained statistically significant after multivariable adjustment (χ(2) = 28.3; P = 0.03), and appeared to be driven by ART-induced improvements in HIV symptom burden, physical and psychological wellbeing, and depression symptom severity.
Figures
References
-
- Palar K, Wagner G, Ghosh-Dastidar B, Mugyenyi P. Role of antiretroviral therapy in improving food security among patients initiating HIV treatment and care in Uganda. AIDS. 2012;26(18):2375–81. - PubMed
-
- Wagner GJ, Ghosh-Dastidar B, Garnett J, Kityo C, Mugyenyi P. Impact of HIV antiretroviral therapy on depression and mental health among clients With HIV in Uganda. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(9):883–90. - PubMed
-
- Rabkin JG, Ferrando SJ, Lin SH, Sewell M, McElhiney M. Psychological effects of HAART: a 2-year study. Psychosom Med. 2000;62(3):413–22. - PubMed
-
- Brent RJ. The effects of HIV medications on the quality of life of older adults in New York City. Health Econ. 2012;21(8):967–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 MH-087228/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH-096620/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH079713/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH-079713/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH087227/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH087228/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH096620/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH-087227/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH-054907/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH054907/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI-027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH-079713-03S1/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical