Prolonged running, not fluoxetine treatment, increases neurogenesis, but does not alter neuropathology, in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 23670818
- PMCID: PMC4554490
- DOI: 10.1007/7854_2012_237
Prolonged running, not fluoxetine treatment, increases neurogenesis, but does not alter neuropathology, in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
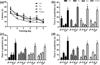
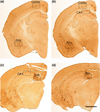
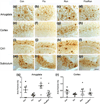
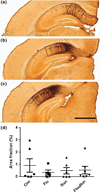
Reductions in adult neurogenesis have been documented in the original 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), notably occurring at the same age when spatial memory deficits and amyloid plaque pathology appeared. As this suggested reduced neurogenesis was associated with behavioral deficits, we tested whether activity and pharmacological stimulation could prevent memory deficits and modify neurogenesis and/or neuropathology in the 3xTg model backcrossed to the C57Bl/6 strain. We chronically administered the antidepressant fluoxetine to one group of mice, allowed access to a running wheel in another, and combined both treatments in a third cohort. All treatments lasted for 11 months. The female 3xTg mice failed to exhibit any deficits in spatial learning and memory as measured in the Morris water maze, indicating that when backcrossed to the C57Bl/6 strain, the 3xTg mice lost the behavioral phenotype that was present in the original 3xTg mouse maintained on a hybrid background. Despite this, the backcrossed 3xTg mice expressed prominent intraneuronal amyloid beta (Aβ) levels in the cortex and amygdala, with lower levels in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. In the combined cohort, fluoxetine treatment interfered with exercise and reduced the total distance run. The extent of Aβ neuropathology, the tau accumulations, or BDNF levels, were not altered by prolonged exercise. Thus, neuropathology was present but not paralleled by spatial memory deficits in the backcrossed 3xTg mouse model of AD. Prolonged exercise for 11 months did improve the long-term survival of newborn neurons generated during middle-age, whereas fluoxetine had no effect. We further review and discuss the relevant literature in this respect.
Figures
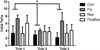
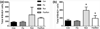
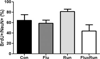
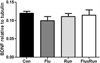
Similar articles
-
Voluntary Running Attenuates Memory Loss, Decreases Neuropathological Changes and Induces Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Pathol. 2016 Jan;26(1):62-74. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12255. Epub 2015 May 7. Brain Pathol. 2016. PMID: 25763997 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of exercise training against the progression of Alzheimer's disease in 3xTg-AD mice.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Nov 18;374:112105. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112105. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31325514
-
Ultrasound with microbubbles improves memory, ameliorates pathology and modulates hippocampal proteomic changes in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Theranostics. 2020 Sep 26;10(25):11794-11819. doi: 10.7150/thno.44152. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33052247 Free PMC article.
-
Depression and adult neurogenesis: Positive effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine and of physical exercise.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Oct;143:181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 30236533 Review.
-
Alcohol drinking exacerbates neural and behavioral pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:169-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.10.017. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physical Activity Ameliorates Impaired Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Tg4-42 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.ASN Neuro. 2019 Jan-Dec;11:1759091419892692. doi: 10.1177/1759091419892692. ASN Neuro. 2019. PMID: 31818124 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Spatial Reorientation in the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1311. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37151-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718609 Free PMC article.
-
Citalopram attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation and spatial memory deficit induced by social isolation rearing in middle-aged rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 May;56(1):145-53. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0475-4. Epub 2014 Dec 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25476250
-
Fluoxetine effects on molecular, cellular and behavioral endophenotypes of depression are driven by the living environment.Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;22(4):552-561. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.142. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 26645631 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Decline in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease: Amyloid-Beta versus Tauopathy.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(1):265-281. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170490. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29154274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, LaFerla FM. Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron. 2005;45(5):675–688. - PubMed
-
- Boekhoorn K, Joels M, Lucassen PJ. Increased proliferation reflects glial and vascular-associated changes, but not neurogenesis in the presenile Alzheimer hippocampus. Neurobiol Dis. 2006a;24(1):1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

