The role of placental protein 14 in the pathogenesis of endometriosis
- PMID: 23670949
- PMCID: PMC3817670
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719113488452
The role of placental protein 14 in the pathogenesis of endometriosis
Abstract
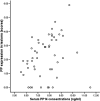
Placental protein 14 (PP-14) is the principal secretory phase product of endometrium and has been shown to inhibit cell immune function. But its role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis is controversy. The objective of this study is to determine the concentrations of PP-14 in peritoneal fluid (PF) and serum and PP-14 protein expression in endometriotic lesions in women with ovarian endometriosis (n = 75) when compared to women without endometriosis (n = 49) between day 7 and day 20 of their menstrual cycle. Concentrations of PP-14 in PF and serum as well as PP-14 protein expression in endometriotic lesions in women with and without endometriosis were evaluated by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunohistochemical staining, respectively. Serum PP-14 concentrations were significantly increased in women with endometriosis (7.5 ± 1.4 ng/mL) compared to those in women without endometriosis (5.8 ± 0.9 ng/mL; P < .05) and statistically decreased after surgery and further reduced by using gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy (P < .05). However, the concentrations of PP-14 in PF did not reach a significant difference between women with and without endometriosis (P > .05). In women with endometriosis, scores of PP-14 protein expression in the lesions (n = 50, 2.2 [0~5.8]) were significantly correlated with serum PP-14 concentrations (n = 50, 7.6 ± 1.3 ng/mL; P < .01). Our results suggest that PP-14 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis.
Keywords: endometriosis; endometrium; peritoneal fluid; placental protein 14; serum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Portelli M, Pollacco J, Sacco K, Schembri-Wismayer P, Calleja-Agius J. Endometrial seedlings. A survival instinct? Immunomodulation and its role in the pathophysiology of endometriosis. Minerva Ginecol. 2011;63(6):563–570. - PubMed
-
- Christodoulakos G, Augoulea A, Lambrinoudaki I, Sioulas V, Creatsas G. Pathogenesis of endometriosis: the role of defective ‘immunosurveillance'. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2007;12(3):194–202. - PubMed
-
- Siristatidis C, Nissotakis C, Chrelias C, Iacovidou H, Salamalekis E. Immunological factors and their role in the genesis and development of endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2006;32(2):162–170. - PubMed
-
- Bersinger NA, Birkhäuser MH, Yared M, Wunder DM. Serum glycodelin pattern during the menstrual cycle in healthy young women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009;88(11):1215–1221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

