Tumor necrosis factor α-induced hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-β-catenin axis regulates major histocompatibility complex class I gene activation through chromatin remodeling
- PMID: 23671189
- PMCID: PMC3700138
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01254-12
Tumor necrosis factor α-induced hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-β-catenin axis regulates major histocompatibility complex class I gene activation through chromatin remodeling
Abstract
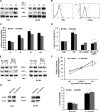
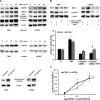
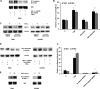
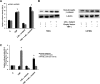
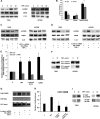
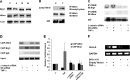
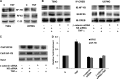
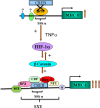
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) plays a crucial role in the progression of glioblastoma multiforme tumors, which are characterized by their effective immune escape mechanisms. As major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) is involved in glioma immune evasion and since HIF-1α is a pivotal link between inflammation and glioma progression, the role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)-induced inflammation in MHC-I gene regulation was investigated. A TNF-α-induced increase in MHC-I expression and transcriptional activation was concurrent with increased HIF-1α, ΝF-κΒ, and β-catenin activities. While knockdown of HIF-1α and β-catenin abrogated TNF-α-induced MHC-I activation, NF-κB had no effect. β-Catenin inhibition abrogated HIF-1α activation and vice versa, and this HIF-1α-β-catenin axis positively regulated CREB phosphorylation. Increased CREB activation was accompanied by its increased association with β-catenin and CBP. Chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed increased CREB enrichment at CRE/site α on the MHC-I promoter in a β-catenin-dependent manner. β-Catenin replaced human Brahma (hBrm) with Brg1 as the binding partner for CREB at the CRE site. The hBrm-to-Brg1 switch is crucial for MHC-I regulation, as ATPase-deficient Brg1 abolished TNF-α-induced MHC-I expression. β-Catenin also increased the association of MHC-I enhanceosome components RFX5 and NF-YB at the SXY module. CREB acts as a platform for assembling coactivators and chromatin remodelers required for MHC-I activation in a HIF-1α/β-catenin-dependent manner.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BRG1 and BRM chromatin-remodeling complexes regulate the hypoxia response by acting as coactivators for a subset of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor target genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;33(19):3849-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00731-13. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23897427 Free PMC article.
-
Ras regulates interleukin-1β-induced HIF-1α transcriptional activity in glioblastoma.J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Feb;89(2):123-36. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0683-5. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20865400
-
Coordinated transcriptional regulation of Hspa1a gene by multiple transcription factors: crucial roles for HSF-1, NF-Y, NF-κB, and CREB.J Mol Biol. 2014 Jan 9;426(1):116-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Sep 14. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24041570
-
Insights on biology and pathology of HIF-1α/-2α, TGFβ/BMP, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF-κB pathways in osteoarthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(22):3293-312. doi: 10.2174/1381612811209023293. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22646092 Review.
-
Regulation of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) by Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines.Cells. 2021 Sep 7;10(9):2340. doi: 10.3390/cells10092340. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRMT1 driven PTX3 regulates ferritinophagy in glioma.Autophagy. 2023 Jul;19(7):1997-2014. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2165757. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36647288 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1 Disrupts PKM2-β-Catenin-BRG1 Transcriptional Network-Driven CD47 Expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Apr 16;38(9):e00001-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00001-18. Print 2018 May 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29463646 Free PMC article.
-
Abrogation of IFN-γ Signaling May not Worsen Sensitivity to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 6;21(5):1806. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051806. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32155707 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immunity and inflammation by hypoxia in immunological niches.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Dec;17(12):774-785. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.103. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28972206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARγ regulated CIDEA affects pro-apoptotic responses in glioblastoma.Cell Death Discov. 2015 Nov 23;1:15038. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.38. eCollection 2015. Cell Death Discov. 2015. PMID: 27551468 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
