Analyses of the survival time and the influencing factors of chinese patients with prion diseases based on the surveillance data from 2008-2011
- PMID: 23671608
- PMCID: PMC3645993
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062553
Analyses of the survival time and the influencing factors of chinese patients with prion diseases based on the surveillance data from 2008-2011
Abstract
Background: Prion diseases are kinds of progressive, incurable neurodegenerative disorders. So far, survival time of the patients with these diseases in China is unclear.
Methods: Based upon the surveillance data from Chinese Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) surveillance network from January 2008 to December 2011, a retrospective follow-up survey was performed. The survival times of Chinese patients with prion diseases and the possible influencing factors were analyzed.
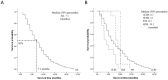
Results: Median survival time of 121 deceased patients was 7.1 months, while those for sporadic CJD (sCJD), familial CJD (fCJD) and fatal familial insomnia (FFI) cases were 6.1, 3.1 and 8.2 months, respectively. 74.0% of sCJD patients, 100% of fCJD cases and 91.7% FFI cases died within one year. The general socio-demographic factors, abnormalities in clinical examinations, clinical manifestations, and social factors did not significantly influence the survival times of Chinese prion patients.
Conclusions: Survival time of Chinese patients with prion diseases was comparable with that of many Western countries, but obviously shorter than that of Japan. Patients with acute onset and rapid progression had significantly short survival times.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory features of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients in China: surveillance data from 2006 to 2010.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024231. Epub 2011 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21904617 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of prion disease is longer in Japan than in other countries.J Epidemiol. 2011;21(4):255-62. doi: 10.2188/jea.je20100085. Epub 2011 May 28. J Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 21628843 Free PMC article.
-
Prion diseases with a focus on Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, a summary of the incidence of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the Czech Republic over the last 17 years, 2000-2017.Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2018 Winter;67(4):155-160. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2018. PMID: 30630318 English.
-
[Surveillance of prion diseases in Japan: analysis of 409 patients].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2003 Nov;43(11):806-9. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2003. PMID: 15152470 Review. Japanese.
-
Epidemiological characteristics of human prion diseases.Infect Dis Poverty. 2016 Jun 2;5(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0143-8. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016. PMID: 27251305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in genetic prion diseases.Brain. 2022 Apr 18;145(2):700-712. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab350. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35288744 Free PMC article.
-
Erythrocyte Indices in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Predict Survival Time.Front Neurol. 2022 Feb 14;13:839081. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.839081. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35237232 Free PMC article.
-
Slow to Respond: A Rapidly Progressive Case of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.Cureus. 2024 Feb 1;16(2):e53381. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53381. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38435214 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Laboratory Features of Three Rare Chinese V210I gCJD Patients.Pathogens. 2020 Sep 28;9(10):800. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9100800. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32998248 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Prion Disease: Insight from the Features and Experience of China National Surveillance for Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.Neurosci Bull. 2021 Nov;37(11):1570-1582. doi: 10.1007/s12264-021-00764-y. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Neurosci Bull. 2021. PMID: 34487324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Will RG (2003) Acquired prion disease: iatrogenic CJD, variant CJD, kuru. Br Med Bull 66: 255–265. - PubMed
-
- Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SN, Estibeiro K, et al. (1996) A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet 347: 921–925. - PubMed
-
- Budka H, Aguzzi A, Brown P, Brucher JM, Bugiani O, et al. (1995) Neuropathological diagnostic criteria for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases). Brain Pathol 5: 459–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

