Simulation techniques in hyperthermia treatment planning
- PMID: 23672453
- PMCID: PMC3711016
- DOI: 10.3109/02656736.2013.790092
Simulation techniques in hyperthermia treatment planning
Abstract
Abstract Clinical trials have shown that hyperthermia (HT), i.e. an increase of tissue temperature to 39-44 °C, significantly enhance radiotherapy and chemotherapy effectiveness [1]. Driven by the developments in computational techniques and computing power, personalised hyperthermia treatment planning (HTP) has matured and has become a powerful tool for optimising treatment quality. Electromagnetic, ultrasound, and thermal simulations using realistic clinical set-ups are now being performed to achieve patient-specific treatment optimisation. In addition, extensive studies aimed to properly implement novel HT tools and techniques, and to assess the quality of HT, are becoming more common. In this paper, we review the simulation tools and techniques developed for clinical hyperthermia, and evaluate their current status on the path from 'model' to 'clinic'. In addition, we illustrate the major techniques employed for validation and optimisation. HTP has become an essential tool for improvement, control, and assessment of HT treatment quality. As such, it plays a pivotal role in the quest to establish HT as an efficacious addition to multi-modality treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


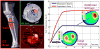
References
-
- van der Zee J. Heating the patient: a promising approach? Ann Oncol. 2002 Aug;13(8):1173–84. - PubMed
-
- Lagendijk JJW, Van den Berg PM, Bach Andersen J, Hand JW, Bardati F, Uzunoglu NK, et al., editors. Treatment planning and modelling in hyperthermia: a task group report. Rome: Tor Vergata, Postgraduate School of Medical Physics, II Universiy of Rome; 1992.
-
- Lagendijk JJ. Hyperthermia treatment planning. Phys Med Biol. 2000 May;45(5):R61–76. - PubMed
-
- Wissler EH. Pennes' 1948 paper revisited. J Appl Physiol. 1998 Jul;85(1):35–41. - PubMed
-
- Bruggmoser G. Some aspects of quality management in deep regional hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28(6):562–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
