Clinical review: Goal-directed therapy-what is the evidence in surgical patients? The effect on different risk groups
- PMID: 23672779
- PMCID: PMC3679445
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11823
Clinical review: Goal-directed therapy-what is the evidence in surgical patients? The effect on different risk groups
Abstract
Patients with limited cardiac reserve are less likely to survive and develop more complications following major surgery. By augmenting oxygen delivery index (DO2I) with a combination of intravenous fluids and inotropes (goal directed therapy (GDT)), postoperative mortality and morbidity of high-risk patients may be reduced. However, although most studies suggest that GDT may improve outcome in high-risk surgical patients, it is still not widely practiced. We set out to test the hypothesis that GDT results in greatest benefit in terms of mortality and morbidity in patients with the highest risk of mortality and have undertaken a systematic review of the current literature to see if this is correct. We performed a systematic search of Medline, Embase and CENTRAL databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and reviews of GDT in surgical patients. To minimize heterogeneity we excluded studies involving cardiac, trauma, and paediatric surgery. Extremely high risk, high risk and intermediate risks of mortality were defined as >20%, 5 to 20% and <5% mortality rates in the control arms of the trials, respectively. Meta analyses were performed and Forest plots drawn using RevMan software. Data are presented as odd ratios (OR; 95% confidence intervals (CI), and P-values). A total of 32 RCTs including 2,808 patients were reviewed. All studies reported mortality. Five studies (including 300 patients) were excluded from assessment of complication rates as the number of patients with complications was not reported. The mortality benefit of GDT was confined to the extremely high-risk group (OR = 0.20, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.41; P < 0.0001). Complication rates were reduced in all subgroups (OR = 0.45, 95% CI 0.34 to 0.60; P < 0.00001). The morbidity benefit was greatest amongst patients in the extremely high-risk subgroup (OR = 0.27, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.51; P < 0.0001), followed by the intermediate risk subgroup (OR = 0.43, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.67; P = 0.0002), and the high-risk subgroup (OR 0.56, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.89; P = 0.01). Despite heterogeneity in trial quality and design, we found GDT to be beneficial in all high-risk patients undergoing major surgery. The mortality benefit of GDT was confined to the subgroup of patients at extremely high risk of death. The reduction of complication rates was seen across all subgroups of GDT patients.
Figures
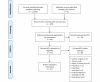
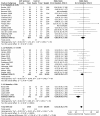
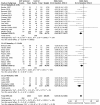
References
-
- Cullinane M, Gray A, Hargraves C, Lansdown M, Martin I, Schubert M. Who Operates When? II. The 2003 Report of the National Confidential Enquiry into Peri-operative Deaths. http://www.ncepod.org.uk/2003wow.htm
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

