Adaptive β-cell proliferation increases early in high-fat feeding in mice, concurrent with metabolic changes, with induction of islet cyclin D2 expression
- PMID: 23673159
- PMCID: PMC3725565
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00040.2013
Adaptive β-cell proliferation increases early in high-fat feeding in mice, concurrent with metabolic changes, with induction of islet cyclin D2 expression
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum for Stamateris et al., volume 305, 2013, p. E149-E159.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Feb 1;326(2):E148. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00040.2023_COR. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38329433 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
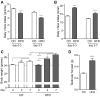
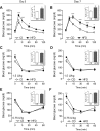
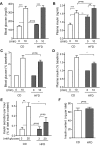
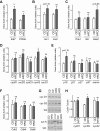
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is caused by relative insulin deficiency, due in part to reduced β-cell mass (11, 62). Therapies aimed at expanding β-cell mass may be useful to treat T2D (14). Although feeding rodents a high-fat diet (HFD) for an extended period (3-6 mo) increases β-cell mass by inducing β-cell proliferation (16, 20, 53, 54), evidence suggests that adult human β-cells may not meaningfully proliferate in response to obesity. The timing and identity of the earliest initiators of the rodent compensatory growth response, possible therapeutic targets to drive proliferation in refractory human β-cells, are not known. To develop a model to identify early drivers of β-cell proliferation, we studied mice during the first week of HFD exposure, determining the onset of proliferation in the context of diet-related physiological changes. Within the first week of HFD, mice consumed more kilocalories, gained weight and fat mass, and developed hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and glucose intolerance due to impaired insulin secretion. The β-cell proliferative response also began within the first week of HFD feeding. Intriguingly, β-cell proliferation increased before insulin resistance was detected. Cyclin D2 protein expression was increased in islets by day 7, suggesting it may be an early effector driving compensatory β-cell proliferation in mice. This study defines the time frame and physiology to identify novel upstream regulatory signals driving mouse β-cell mass expansion, in order to explore their efficacy, or reasons for inefficacy, in initiating human β-cell proliferation.
Keywords: diet-induced obesity; islet replication; overnutrition; pancreatic β-cell mitosis; short-term high-fat diet.
Figures



References
-
- Ahren B, Gudbjartsson T, Al-Amin AN, Martensson H, Myrsen-Axcrona U, Karlsson S, Mulder H, Sundler F. Islet perturbations in rats fed a high-fat diet. Pancreas 18: 75–83, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ahren B, Pacini G. Insufficient islet compensation to insulin resistance vs. reduced glucose effectiveness in glucose-intolerant mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283: E738–E744, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Ahren J, Ahren B, Wierup N. Increased beta-cell volume in mice fed a high-fat diet: a dynamic study over 12 months. Islets 2: 353–356, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Alonso LC, Watanabe Y, Stefanovski D, Lee EJ, Singamsetty S, Romano LC, Zou B, Garcia-Ocana A, Bergman RN, O'Donnell CP. Simultaneous measurement of insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and the disposition index in conscious unhandled mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20: 1403–1412, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

