Endolysosome involvement in HIV-1 transactivator protein-induced neuronal amyloid beta production
- PMID: 23673310
- PMCID: PMC3706576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.04.015
Endolysosome involvement in HIV-1 transactivator protein-induced neuronal amyloid beta production
Abstract
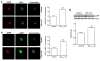
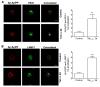
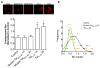
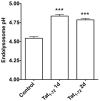
The increased life expectancy of people living with HIV-1/AIDS is accompanied by increased prevalence of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorder. As well, these individuals are increasingly experiencing Alzheimer's disease (AD)-like neurocognitive problems and neuropathological features such as increased deposition of amyloid beta (Aβ) protein. Findings that Aβ production occurs largely in endolysosomes, that HIV-1 transactivator protein (Tat) disrupts endolysosome function-an early pathological feature of AD-and that HIV-1 Tat can increase Aβ levels prompted us to test the hypothesis that endolysosome dysfunction is associated with HIV-1 Tat-induced increases in neuronal Aβ generation. Using primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons, we found that treatment with HIV-1 Tat caused such morphological changes as enlargement of endolysosomes identified with LysoTracker dye and such functional changes as elevated endolysosome pH measured ratiometrically with LysoSensor dye. The HIV-1 Tat-induced changes in endolysosome function preceded temporally HIV-1 Tat-induced increases in Aβ generation measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In addition, we demonstrated that HIV-1 Tat increased endolysosome accumulation of Aβ precursor protein and Aβ identified using immunostaining with 4G8 antibodies. Furthermore, we demonstrated that treatment of neurons with HIV-1 Tat increased endolysosome accumulation of beta amyloid-converting enzyme, the rate-limiting enzymatic step for Aβ production, and enhanced beta amyloid-converting enzyme activity. Together, our findings suggest that HIV-1 Tat increases neuronal Aβ generation and thereby contributes to the development of AD-like pathology in HIV-1-infected individuals by disturbing endolysosome structure and function.
Keywords: Amyloid beta; BACE-1; Endolysosome; HIV-1 Tat; pH.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no current or potential conflicts of interest to report.
The authors have no current or potential conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
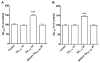
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

