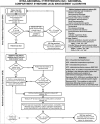
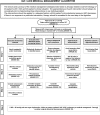
Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome: updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
- PMID: 23673399
- PMCID: PMC3680657
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-2906-z
Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome: updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abstract
Purpose: To update the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome (WSACS) consensus definitions and management statements relating to intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and the abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS).
Methods: We conducted systematic or structured reviews to identify relevant studies relating to IAH or ACS. Updated consensus definitions and management statements were then derived using a modified Delphi method and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) guidelines, respectively. Quality of evidence was graded from high (A) to very low (D) and management statements from strong RECOMMENDATIONS (desirable effects clearly outweigh potential undesirable ones) to weaker SUGGESTIONS (potential risks and benefits of the intervention are less clear).
Results: In addition to reviewing the consensus definitions proposed in 2006, the WSACS defined the open abdomen, lateralization of the abdominal musculature, polycompartment syndrome, and abdominal compliance, and proposed an open abdomen classification system. RECOMMENDATIONS included intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) measurement, avoidance of sustained IAH, protocolized IAP monitoring and management, decompressive laparotomy for overt ACS, and negative pressure wound therapy and efforts to achieve same-hospital-stay fascial closure among patients with an open abdomen. SUGGESTIONS included use of medical therapies and percutaneous catheter drainage for treatment of IAH/ACS, considering the association between body position and IAP, attempts to avoid a positive fluid balance after initial patient resuscitation, use of enhanced ratios of plasma to red blood cells and prophylactic open abdominal strategies, and avoidance of routine early biologic mesh use among patients with open abdominal wounds. NO RECOMMENDATIONS were possible regarding monitoring of abdominal perfusion pressure or the use of diuretics, renal replacement therapies, albumin, or acute component-parts separation.
Conclusion: Although IAH and ACS are common and frequently associated with poor outcomes, the overall quality of evidence available to guide development of RECOMMENDATIONS was generally low. Appropriately designed intervention trials are urgently needed for patients with IAH and ACS.
Figures
References
-
- Kimball EJ, Kim W, Cheatham ML, Malbrain ML (2007) Clinical awareness of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in 2007. Acta Clin Belg (Suppl): 66–73 - PubMed
-
- Malbrain ML, Cheatham ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M, De Waele J, Balogh Z, Leppaniemi A, Olvera C, Ivatury R, D’Amours S, Wendon J, Hillman K, Johansson K, Kolkman K, Wilmer A. Results from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. I. Definitions. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32:1722–1732. doi: 10.1007/s00134-006-0349-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Malbrain ML, Cheatham ML. Definitions and pathophysiological implications of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. Am Surg. 2011;77(Suppl 1):6–11. - PubMed
-
- Cheatham ML, Malbrain ML, Kirkpatrick A, Sugrue M, Parr M, De Waele J, Balogh Z, Leppaniemi A, Olvera C, Ivatury R, D’Amours S, Wendon J, Hillman K, Wilmer A. Results from the international conference of experts on intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. II. Recommendations. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:951–962. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0592-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials