Detection and characterization of nocardia from patients diagnosed as tuberculosis in egypt
- PMID: 23675087
- PMCID: PMC3614701
Detection and characterization of nocardia from patients diagnosed as tuberculosis in egypt
Abstract
Pulmonary tuberculosis and pulmonary nocardiosis are similar in most clinical symptoms and radiological manifestation. In the developing countries like Egypt where tuberculosis is very common, anti-tuberculosis drugs are started on basis of radiology and clinical symptoms. This study included 600 sputum specimens collected from 200 patients diagnosed as pulmonary tuberculosis from three chest hospitals in Egypt. IS6110 specific primer were selected for PCR to identify the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and hsp65 gene specific primers were used for PCR and sequencing for the identification of Mycobacterium and Nocardial species. The region of the gene coding for 16S rRNA in Nocardia species were selected as genus specific primer sequences for a PCR and Real Time PCR assays. Our result confirmed that four whole DNA samples, extracted from sputum specimen from the pulmonary tuberculosis patients on anti-tuberculosis treatment, were Nocardia species. Three of them matched (99% homology) with Nocardia farcinica (formerly Nocardia asteroid type V) and one match (83% homology) with Nocardia pneumonia. Molecular methods such as PCR and real-time PCR for identification of Nocardia are rapid and accurate methods. No cross-reactions were observed using Real Time PCR specific for Nocordia with other closely related genera.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Nocardia; real time PCR.
Figures

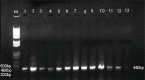


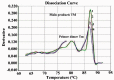
References
-
- Centers for disease control and prevention (CDC) Nocardiosis, Division of bacterial and mycotic disease. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/nocardiosis_t.htm . 2005
-
- Kageyama A, Yazawa K, Ishikawa J, Hotta K, et al. Nocardial infection in Japan from 1992 to 2001, including the first report of infection by Nocardia transvalensis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004;19:383–389. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
