A Validated Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Antidiabetic Agent Pioglitazone HCl in Tablets and Biological Fluids
- PMID: 23675103
- PMCID: PMC3614714
A Validated Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Antidiabetic Agent Pioglitazone HCl in Tablets and Biological Fluids
Abstract
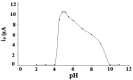
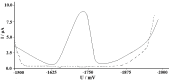
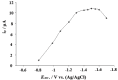
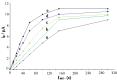
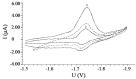
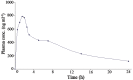
Square-wave adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry was used to determine pioglitazone HCl in Britton Robinson buffer of pH5. The adsorptive cathodic peak was observed at -1.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The peak response was characterized with respect to pH, supporting electrolyte, frequency, scan increment, pulse-amplitude, accumulation potential and pre-concentration time. Under optimal conditions, the peak current is proportional to the concentration of pioglitazone HCl, and a linear calibration graphs were obtained within the concentration levels of 10(-8) and 10(-4) M following different accumulation time periods (0-300 s). The obtained results were analyzed and the statistical parameters were calculated. The detection limit is 8.08 × 10(-9) M (3.17 ng ml(-1)) using 300 s pre-concentration time, whereas the quantitative limit is 2.45 × 10(-8) M (9.63 ng ml(-1)). The proposed method was applied to assay the drug in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids. The pharmacokinetic parameters of drug in human plasma were estimated as: C max=785.8 ng ml(-1), t max=1.5 h, K e=0.125 h(-1) and t 1/2=8 h which are favorably compared with those reported in literature.
Keywords: actos tablets; adsorptive stripping voltammetry; biological fluids; pharmacokinetic; pioglitazone HCl; square-wave.
Figures
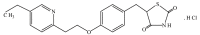
Similar articles
-
Adsorptive stripping anodic voltammetric determination of thioctic Acid in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations.Int J Biomed Sci. 2009 Mar;5(1):54-8. Int J Biomed Sci. 2009. PMID: 23675115 Free PMC article.
-
Voltammetric determination of cefixime in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids.Anal Biochem. 2010 Dec 1;407(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.07.027. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Anal Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20678464
-
Development of square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for determination of acebutolol in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids.Chem Cent J. 2012 Feb 21;6:15. doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-15. Chem Cent J. 2012. PMID: 22353684 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of the anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib in pharmaceutical formulation and human serum.Talanta. 2003 Jul 27;60(5):911-21. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(03)00151-6. Talanta. 2003. PMID: 18969115
-
Voltammetric determination of cilazapril in pharmaceutical formulations.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002 Jun 20;29(1-2):43-50. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(02)00033-x. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002. PMID: 12062663
Cited by
-
HPLC-DAD Method for the Pharmacokinetic Interaction Study of Atorvastatin with Pioglitazone and Cholestyramine in Wistar Rats.Sci Pharm. 2014 Mar 13;82(3):555-70. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1401-18. Print 2014 Jul-Sep. Sci Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25853068 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Assays for the Determination of Antidiabetic Drugs-A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;15(1):10. doi: 10.3390/mi15010010. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38276837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sohda T, Mizuno K, Momose Y, Ikeda H, et al. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:2617–2626. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi M, Iwanishi M, Egawa K, Shigeta Y. Diabetes. 1992;41:476–483. - PubMed
-
- Waugh J, Keating GM, Plosker GL, Easthope S. Drugs. 2006;66:85–109. - PubMed
-
- Chilcott J, Tappenden P, Lloyd M, Wight JP. Clin. Ther. 2001;23:1792–1823. - PubMed
-
- Giaginis C, Theocharis S, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A. J. Chromatogr. B. 2007;857:181–187. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
