Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
- PMID: 23675141
- PMCID: PMC3614782
Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the kinetics of molecular response to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) therapy in predicting progression free survival (PFS), sustained hematological, and cytogenetic responses in CPCML.
Methods: Ninety five newly diagnosed CPCML Egyptian patients were treated with IM 400 mg daily dose. Cytogenetic analysis was performed at diagnosis and every 6 months. Molecular monitoring by RT-QPCR was performed at diagnosis and every 3 months during a median follow-up period (FUp) of 26 months. Mutation detection of ABL domain was performed by ASO-PCR.
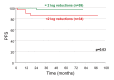
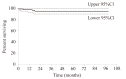
Results: Hematological response was 98% after three months of IM therapy. Out of 95 patients 59 showed 2 log reduction of BCR-ABL/ABL ratio after 6 months of whom 49 (83%) had complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) and 42 (71%) had major molecular response (MMR) at 12 months. BCR-ABL transcripts remained undetectable in 22 patients (39%) at 26 months. Among the remaining 34 patients not achieving 2 log reduction at 6 months only 5 (15%) had CCyR and MMR by 12 months. ABL domain mutations were detected in 11/15 (73%) resistant and suboptimal responding patients. Achieving 2 log reduction after 6 months of IM therapy significantly correlated with sustained cytogenetic and molecular responses (p<0.0001), with PFS at 2 years (p<0.03) and inversely with ABL gene mutations (p<0.001).
Discussion: These data demonstrated the predictive value of early molecular response to IM in CPCML regarding disease course and PFS. A 2 log reduction at 6 months of IM treatment could be a cut off level predicting resistance, CCyR, or suggesting IM dose modification.
Keywords: ABL kinase mutations; CML; cytogenetic responses; imatinib mesylate; molecular responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Value of Pretreatment BCR-ABL(IS) Transcript level on Response to Imatinib Therapy in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CPCML).Int J Biomed Sci. 2013 Mar;9(1):48-53. Int J Biomed Sci. 2013. PMID: 23675289 Free PMC article.
-
[A clinical and laboratory study of chronic myeloid leukemia with atypical BCR-ABL fusion gene subtypes].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;35(3):210-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2014.03.007. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24666486 Chinese.
-
[Therapeutic Effect of Imatinib Made in Real World to Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Apr;29(2):456-461. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2021.02.024. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33812415 Chinese.
-
Monitoring minimal residual disease in BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era.Curr Opin Hematol. 2005 Jan;12(1):33-9. doi: 10.1097/01.moh.0000148551.93303.9e. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15604889 Review.
-
Roots of imatinib resistance: a question of self-renewal?Drug Resist Updat. 2007 Aug-Oct;10(4-5):152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Drug Resist Updat. 2007. PMID: 17683977 Review.
Cited by
-
Trial Design and Statistical Considerations on the Assessment of Pharmacodynamic Similarity.AAPS J. 2019 Apr 3;21(3):47. doi: 10.1208/s12248-019-0321-2. AAPS J. 2019. PMID: 30945035
-
Predictive Value of Pretreatment BCR-ABL(IS) Transcript level on Response to Imatinib Therapy in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CPCML).Int J Biomed Sci. 2013 Mar;9(1):48-53. Int J Biomed Sci. 2013. PMID: 23675289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melo JV. The diversity of BCR-ABL fusion proteins and their relationship to leukemia phenotype. Blood. 1996;319:990. - PubMed
-
- Sawyers CL. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:1330. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of bcr abl tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. England J. Med. 2001;344:1031. - PubMed
-
- Hochhaus A, Druker BJ, Larson RA, O'Brien SG, et al. IRIS 6-Year Follow up: Sustained survival and declining Annual rate of transformation in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with imatinib. Blood. 2007;110(11) [abstract 25]
-
- Cortes J, Talpaz M, O'Brien S, Jones D, et al. Molecular responses in patients with chronic Myelogenous Leukemia in Chronic phase treated with Imatinib Mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11(9):3425. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous