The effect of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell to erythroid lineage in serum free and serum supplemented media
- PMID: 23675148
- PMCID: PMC3614786
The effect of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell to erythroid lineage in serum free and serum supplemented media
Abstract
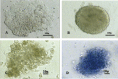
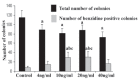
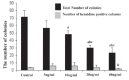
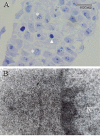
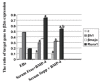
This study was done to compare the effects of bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) on mouse embryonic stem cells (ESC) differentiation to erythroid lineage in serum free and serum supplemented media. The embryoid bodies (EBs) cells were seeded in semisolid serum free and serum supplemented media in the presence of different concentrations of BMP-4. The erythroid colonies were assessed morphologically, ultrastructurally and by benzidine staining. The expression of the epsilon (ε), βH1 and βmajor globins, Runx1 and β2m genes was evaluated by Real time PCR. The colony size and the percent of benzidine-positive colonies increased in both BMP-4 supplementd groups but the number of colonies were lower in these groups than control. Erythropoiesis related genes were expressed in both serum free and serum supplemented groups. There were not significant differences between the ratios of genes expression to β2m in these groups except the ratio of Runx1 was significantly higher in serum free group (P<0.05). The ratio of ε and βH1 to β2m in EBs was higher than both BMP-4 containing groups (P<0.05) and βmajor was not expressed in EB cells. These findings showed in serum free condition the effects of BMP-4 on the erythroid differentiation was prominent than serum supplemented group.
Keywords: bone morphogenetic protein-4; embryonic stem cells; erythropoiesis; serum free media.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of gene expression profiles in erythroid-like cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells differentiated in simple and co-culture systems.Am J Hematol. 2008 Feb;83(2):109-15. doi: 10.1002/ajh.21037. Am J Hematol. 2008. PMID: 17712792
-
Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-4 on cardiac differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cells in serum-free and low-serum media.Int J Cardiol. 2008 Jun 23;127(1):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.04.173. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Int J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 17714812
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-4 promotes induction of cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cells in serum-based embryoid body development.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):H1793-803. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01288.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19363129
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins act synergistically with haematopoietic cytokines in the differentiation of haematopoietic progenitors.Cytokine. 2002 Jan 7;17(1):36-42. doi: 10.1006/cyto.2001.0984. Cytokine. 2002. PMID: 11886169
-
Analysis of the temporal and concentration-dependent effects of BMP-4, VEGF, and TPO on development of embryonic stem cell-derived mesoderm and blood progenitors in a defined, serum-free media.Exp Hematol. 2008 Sep;36(9):1186-98. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Exp Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18550259
Cited by
-
Protective effects of melatonin and ghrelin on spermatogenesis: A narrative review of the literature.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017 May;15(5):265-272. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28744521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pearson S, Sroczynska P, Lacaud G, Kouskoff V. The stepwise specification of embryonic stem cells to hematopoietic fate is driven by sequential exposure to BMP-4, activin A, bFGF and VEGF. Development. 2008;135(8):1525. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
