Long Term Persistence of IgE Anti-Varicella Zoster Virus in Pediatric and Adult Serum Post Chicken Pox Infection and after Vaccination with Varicella Virus Vaccine
- PMID: 23675158
- PMCID: PMC3614806
Long Term Persistence of IgE Anti-Varicella Zoster Virus in Pediatric and Adult Serum Post Chicken Pox Infection and after Vaccination with Varicella Virus Vaccine
Abstract
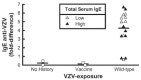
The production of IgE specific to different viruses (HIV-1, Parvovirus B19, RSV), and the ability for IgE anti-HIV-1 to suppress HIV-1 production in vitro, strongly suggest an important role for IgE and/or anti viral specific IgE in viral pathogenesis. Previous studies in our laboratory were the first to report the presence of IgE anti-varicella zoster virus (VZV) in an adolescent patient with shingles. However, the presence and long term persistence of IgE anti VZV antibodies has not been studied in adults. The presence of serum IgE in addition to IgE and IgG anti-VZV antibody in sera were studied in children (N=12) (0-16 y/o) and adults (N=9) (32-76 y/o) with either a past history of (wild type) chicken pox (N=7 children, 9 adults) or 5 years after vaccination with varicella zoster (N=2 children) (Varicella virus vaccine live, Oka/Merck), as well as in non-infected subjects (N=3 children). Of the patients who had a positive history of chicken pox 13 of 16 (81%) contained IgE anti-VZV antibodies; they were both serum IgEHi (>100 IU/ml) and IgELo (<100 IU/ml). Of the patients who were vaccinated, IgE anti-VZV antibodies were undetected. In contrast, serum from the patients without a history of chicken pox or vaccination did not make either IgE or IgG anti-VZV antibodies. This is the first demonstration of the existence of IgE anti-VZV antibodies, and its long-term persistence in serum of previously infected subjects. Future studies regarding the functional role of anti-viral IgE and its relationship to VZV are warranted.
Keywords: IgE; varicella zoster virus; varicella zoster virus vaccine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Negative IgG Varicella Zoster Virus Antibody Status: Immune Responses Pre and Post Re-immunization.Infect Dis Ther. 2018 Mar;7(1):175-181. doi: 10.1007/s40121-017-0182-x. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Infect Dis Ther. 2018. PMID: 29273977 Free PMC article.
-
Long term persistence of IgE anti-influenza virus antibodies in pediatric and adult serum post vaccination with influenza virus vaccine.Int J Med Sci. 2011 Mar 18;8(3):239-44. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8.239. Int J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21448311 Free PMC article.
-
IgE anti-varicella zoster virus and other immune responses before, during, and after shingles.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2009 Winter;39(1):43-50. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2009. PMID: 19201740
-
Varicella-zoster virus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996 Jul;9(3):361-81. doi: 10.1128/CMR.9.3.361. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996. PMID: 8809466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Varicella-zoster virus infection: natural history, clinical manifestations, immunity and current and future vaccination strategies.New Microbiol. 2018 Apr;41(2):95-105. Epub 2018 Mar 2. New Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29498740 Review.
Cited by
-
An unexpected IgE anti-receptor binding domain response following natural infection and different types of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):20003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71047-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39198569 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of Disease Manifestations in Patients with Selective Immunoglobulin E Deficiency.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 15;10(18):4160. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184160. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575269 Free PMC article.
-
Blood parameters differentiate post COVID-19 condition from Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Jul 4;48:101058. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101058. eCollection 2025 Oct. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40726775 Free PMC article.
-
Negative IgG Varicella Zoster Virus Antibody Status: Immune Responses Pre and Post Re-immunization.Infect Dis Ther. 2018 Mar;7(1):175-181. doi: 10.1007/s40121-017-0182-x. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Infect Dis Ther. 2018. PMID: 29273977 Free PMC article.
-
Increased seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 IgE antibodies in asthmatic compared with non-asthmatic children.Ir J Med Sci. 2017 May;186(2):495-503. doi: 10.1007/s11845-016-1480-0. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Ir J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27440276
References
-
- Bluth MH, Norowitz KB, Chice S, Shah VN, et al. Detection of IgE anti-parvovirus B19 and increased CD23+ B cells in parvovirus B19 infection: relation to Th2 Cytokines. Clin. Immunol. 2003;108:152–158. - PubMed
-
- Secord EA, Kleiner GI, Auci DL, et al. IgE against HIV proteins in clinically healthy childen with HIV disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996;98:979–984. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrino MG, Bluth MH, Smith-Norowitz TA, et al. HIV-1 Specific IgE in serum of long term surviving children inhibits HIV-1 production in vitro . AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 2002;18:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Lev Tov H, Josekutty J, Kohlhoff S, Norowitz KB, et al. IgE anti-varicella virus (VZV) and other immune responses before, during, and after shingles. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008;121:S207. - PubMed
-
- Smith-Norowitz TA, Josekutty J, Lev-Tov H, Kohlhoff S, et al. IgE anti-Varicella Zoster virus and other immune responses before, during, and after shingles. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009;39(1):43–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
