Statins inhibit the proliferation and induce cell death of human papilloma virus positive and negative cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 23675166
- PMCID: PMC3614803
Statins inhibit the proliferation and induce cell death of human papilloma virus positive and negative cervical cancer cells
Abstract
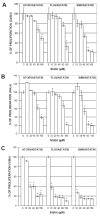
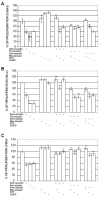
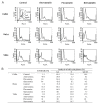
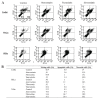
Statins, competitive inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, have anti-tumoral effects on multiple cancer types; however, little is known about their effect on cervical cancer. We evaluated the effect on proliferation, cell cycle, oxidative stress and cell death of three statins on CaSki, HeLa (HPV(+)) and ViBo (HPV(-)) cervical cancer cell lines. Cell proliferation was assayed by crystal violet staining, cell cycle by flow cytometry and cell death by annexin-V staining. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was evaluated by the oxidation of 2,7-dichlorofluorescein diacetate and nitrite concentration (an indirect measure of nitric oxide (NO) production), by the Griess reaction. Inhibition of cell proliferation by atorvastatin, fluvastatin and simvastatin was dose-dependent. ViBo cells were the most responsive. Statins did not affect the cell cycle, instead they induced cell death. The antiproliferative effect in ViBo cells was completely inhibited with mevalonate, farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) treatments. In contrast, cell proliferation of CaSki and HeLa cells was partially (33%) rescued with these intermediates. The three statins increased ROS and nitrite production, mainly in the ViBo cell line. These results suggest that statins exert anti-tumoral effects on cervical cancer through inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of cell death and oxidative stress. Statins could be an aid in the treatment of cervical cancer, especially in HPV(-) tumors.
Keywords: cell cycle; cell death; cervical cancer; human papilloma virus; mevalonate pathway; oxidative stress; proliferation; statins.
Figures
References
-
- Jakobisiak M, Golab J. Potential antitumor effects of statins. Int. J. Oncol. 2003;23:1055. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425. - PubMed
-
- Alegret M, Silvestre JS. Pleiotropic effects of statins and related pharmacological experimental approaches. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006;28:627. - PubMed
-
- Graaf MR, Richel DJ, van Noorden CJ, GucHeLaar HJ. Effects of statins and farnesyltransferase inhibitors on the development and progression of cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004;30:609. - PubMed
-
- Dimitroulakos J, Ye LY, Benzaquen M, Moore MJ, et al. Differential sensitivity of various pediatric cancers and squamous cell carcinomas to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: therapeutic implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001;7:158. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
