Histological and Demographic Characteristics of the Distribution of Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors' Sizes: Results from SEER Registries Using Statistical Methods
- PMID: 23675268
- PMCID: PMC3615278
Histological and Demographic Characteristics of the Distribution of Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors' Sizes: Results from SEER Registries Using Statistical Methods
Abstract
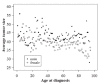
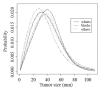
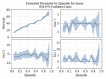
The examination of brain tumor growth and its variability among cancer patients is an important aspect of epidemiologic and medical data. Several studies for tumors of brain interpreted descriptive data, in this study we perform inference in the extent possible, suggesting possible explanations for the differentiation in the survival rates apparent in the epidemiologic data. Population based information from nine registries in the USA are classified with respect to age, gender, race and tumor histology to study tumor size variation. The Weibull and Dagum distributions are fitted to the highly skewed tumor sizes distributions, the parametric analysis of the tumor sizes showed significant differentiation between sexes, increased skewness for both the male and female populations, as well as decreased kurtosis for the black female population. The effect of population characteristics on the distribution of tumor sizes is estimated by quantile regression model and then compared with the ordinary least squares results. The higher quantiles of the distribution of tumor sizes for whites are significantly higher than those of other races. Our model predicted that the effect of age in the lower quantiles of the tumor sizes distribution is negative given the variables race and sex. We apply probability and regression models to explore the effects of demographic and histology types and observe significant racial and gender differences in the form of the distributions. Efforts are made to link tumor size data with available survival rates in relation to other prognostic variables.
Keywords: SEER; brain and CNS; parametric analysis; prognostic variables; quantile regression; survival rate; tumor size.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variation in Breast Cancer Subtype Incidence and Distribution by Race/Ethnicity in the United States From 2010 to 2015.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Oct 1;3(10):e2020303. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.20303. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33074325 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Cell Myeloma - 20-Year Comparative Survival and Mortality of Three Plasma Cell Myeloma ICD-O-3 Oncologic Phenotypes by Age, Sex, Race, Stage, Cohort Entry Time-Period and Disease Duration: A Systematic Review of 111,041 Cases for Diagnosis Years 1973-2014: (SEER*Stat 8.3.4).J Insur Med. 2018;47(4):203-211. doi: 10.17849/insm-47-04-1-9.1. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Insur Med. 2018. PMID: 30668210
-
Primary Central Nervous System Tumors: Comparing Two National Cancer Registries.World Neurosurg. 2019 Aug;128:e719-e731. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.247. Epub 2019 May 8. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31077903
-
Differences in breast cancer hormone receptor status and histology by race and ethnicity among women 50 years of age and older.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002 Jul;11(7):601-7. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002. PMID: 12101106
-
20-Year Comparative Survival and Mortality of Cancer of the Stomach by Age, Sex, Race, Stage, Grade, Cohort Entry Time-Period, Disease Duration & Selected ICD-O-3 Oncologic Phenotypes: A Systematic Review of 157,258 Cases for Diagnosis Years 1973-2014: (SEER*Stat 8.3.4).J Insur Med. 2019;48(1):5-23. doi: 10.17849/insm-48-1-1-19.1. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Insur Med. 2019. PMID: 31609640
Cited by
-
A Biomechanical Model of Tumor-Induced Intracranial Pressure and Edema in Brain Tissue.Biophys J. 2019 Apr 23;116(8):1560-1574. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.02.030. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 30979548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darefsky AS, Dubrow R. Brain tumor epidemiology: Consesus from the brain tumor epidemiology consortium. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20:1593. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Gonzalez MA, Sotelo J. Brain Tumors in Mexico: Characteristics and Prognosis of Glioblastoma. Surgical Neurology. 2000;53(2):157. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer WA. Epidemiologic impact of children with brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst. 1999;15(11-12):758. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
