(31)P and (1)h nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of blood plasma in female patients with preeclampsia
- PMID: 23675281
- PMCID: PMC3615299
(31)P and (1)h nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of blood plasma in female patients with preeclampsia
Abstract
Objective: Using (31)P and (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure phosphorus- and hydrogen-containing metabolites, this study aimes to investigate whether or not women with preeclampsia have detectable systemic abnormalities concerning certain components of the blood plasma.
Methods: PLASMA WAS OBTAINED FROM TWO GROUPS OF WOMEN: Group 1 with preeclampsia (n=10) and Group 2, as a control group with no complications during pregnancy (n=10). Plasma analysis were performed using in-vitro (31)P and (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
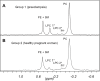
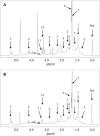
Results: (31)P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra showed significantly higher levels of lysophosphatidylcholine 1 in the plasma of the patients in Group 1, along with significantly decreased levels of lysophosphatidylcholine 2 and phosphatidylinositol. However, the total amount of phospholipids did not differ significantly between the groups. In addition, the (1)H NMR spectra showed a significantly lower level of HDL in samples from Group 1, and a trend towards higher plasma levels of VLDL 2 and LDL 2 in the same group.
Conclusion: This study supports the theory that preeclampsia is a disorder in phospholipid metabolism in which malfunctioning of cellular membranes seems to play a major pathogenic role.
Keywords: 31P and 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy; gestosis; lipid metabolism; preeclampsia.
Figures
References
-
- Chappell LC, Seed PT, Briley AL, et al. Effect of antioxidants on the occurrence of pre-eclampsia in women at increased risk: a randomised trial. Lancet. 1996;354(9181):810–816. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein L. Syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet count: a severe consequence of hypertension in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1982;142:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Vigil-De Gracia P. Pregnancy complicated by pre-eclampsia-eclampsia with HELLP syndrome. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2001;72:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Magann EF, Martin JN. Twelve steps to optimal management of HELLP syndrome. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999;42:532–541. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, Wenzel U, Stahl RAK, Hüneke B. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy (German) Med. Klin. 2001;96:78–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
