Interplay between pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in depressive illnesses
- PMID: 23675319
- PMCID: PMC3650474
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00068
Interplay between pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in depressive illnesses
Abstract
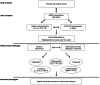
The development of depressive disorders had long been attributed to monoamine variations, and pharmacological treatment strategies likewise focused on methods of altering monoamine availability. However, the limited success achieved by treatments that altered these processes spurred the search for alternative mechanisms and treatments. Here we provide a brief overview concerning a possible role for pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in major depression, as well as the possibility of targeting these factors in treating this disorder. The data suggest that focusing on one or another cytokine or growth factor might be counterproductive, especially as these factors may act sequentially or in parallel in affecting depressive disorders. It is also suggested that cytokines and growth factors might be useful biomarkers for individualized treatments of depressive illnesses.
Keywords: BDNF; antidepressant; depression; growth factors; pro-inflammatory cytokines; stressors.
Figures
References
-
- Aloe L., Bracci-Laudiero L., Alleva E., Lambiase A., Micera A., Tirassa P. (1994). Emotional stress induced by parachute jumping enhances blood nerve growth factor levels and the distribution of nerve growth factor receptors in lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 10440–10444 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

