Altered anxiety-related and abnormal social behaviors in rats exposed to early life seizures
- PMID: 23675329
- PMCID: PMC3648772
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00036
Altered anxiety-related and abnormal social behaviors in rats exposed to early life seizures
Abstract
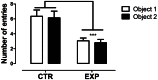
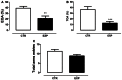
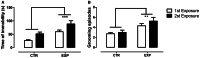
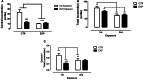
Neonatal seizures are the most common manifestation of neurological dysfunction in the neonate. The prognosis of neonatal seizures is highly variable, and the controversy remains whether the severity, duration, or frequency of seizures may contribute to brain damage independently of its etiology. Animal data indicates that seizures during development are associated with a high probability of long-term adverse effects such as learning and memory impairment, behavioral changes and even epilepsy, which is strongly age dependent, as well as the severity, duration, and frequency of seizures. In preliminary studies, we demonstrated that adolescent male rats exposed to one-single neonatal status epilepticus (SE) episode showed social behavior impairment, and we proposed the model as relevant for studies of developmental disorders. Based on these facts, the goal of this study was to verify the existence of a persistent deficit and if the anxiety-related behavior could be associated with that impairment. To do so, male Wistar rats at 9 days postnatal were submitted to a single episode of SE by pilocarpine injection (380 mg/kg, i.p.) and control animals received saline (0.9%, 0.1 mL/10 g). It was possible to demonstrate that in adulthood, animals exposed to neonatal SE displayed low preference for social novelty, anxiety-related behavior, and increased stereotyped behavior in anxiogenic environment with no locomotor activity changes. On the balance, these data suggests that neonatal SE in rodents leads to altered anxiety-related and abnormal social behaviors.
Keywords: general anxiety; neonatal status epilepticus; pilocarpine; social anxiety; social behavior.
Figures

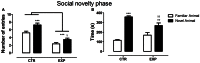
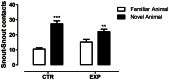
Similar articles
-
Effect of diazepam on sociability of rats submitted to neonatal seizures.Data Brief. 2016 Mar 12;7:686-91. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.03.029. eCollection 2016 Jun. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 27054178 Free PMC article.
-
Early life seizures in female rats lead to anxiety-related behavior and abnormal social behavior characterized by reduced motivation to novelty and deficit in social discrimination.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Mar;122(3):349-55. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1291-2. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015. PMID: 25139483
-
Comorbidities of early-onset temporal epilepsy: Cognitive, social, emotional, and morphologic dimensions.Exp Neurol. 2019 Oct;320:113005. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113005. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31278943
-
Maternal crack cocaine use in rats leads to depressive- and anxiety-like behavior, memory impairment, and increased seizure susceptibility in the offspring.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Mar;44:34-50. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2020.12.011. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33454149
-
Increased Endocannabinoid Signaling Reduces Social Motivation in Intact Rats and Does Not Affect Animals Submitted to Early-Life Seizures.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Dec 9;14:560423. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.560423. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33362484 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
mTOR inhibitor improves autistic-like behaviors related to Tsc2 haploinsufficiency but not following developmental status epilepticus.J Neurodev Disord. 2021 Apr 17;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s11689-021-09357-2. J Neurodev Disord. 2021. PMID: 33863288 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of seizure-induced MeCP2 Ser421 phosphorylation in the developing brain.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Aug;116:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29738885 Free PMC article.
-
A Two-Hit Approach Inducing Flurothyl Seizures in Fmr1 Knockout Mice Impacts Anxiety and Repetitive Behaviors.Brain Sci. 2024 Aug 31;14(9):892. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14090892. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39335388 Free PMC article.
-
Late Effects of 16O-Particle Radiation on Female Social and Cognitive Behavior and Hippocampal Physiology.Radiat Res. 2019 Mar;191(3):278-294. doi: 10.1667/RR15092.1. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 30664396 Free PMC article.
-
Amidated and Ibuprofen-Conjugated Kyotorphins Promote Neuronal Rescue and Memory Recovery in Cerebral Hypoperfusion Dementia Model.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Jan 26;8:1. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00001. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26858637 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

