Structural basis of empathy and the domain general region in the anterior insular cortex
- PMID: 23675334
- PMCID: PMC3648769
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00177
Structural basis of empathy and the domain general region in the anterior insular cortex
Abstract
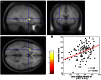
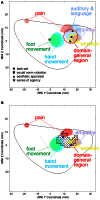
Empathy is key for healthy social functioning and individual differences in empathy have strong implications for manifold domains of social behavior. Empathy comprises of emotional and cognitive components and may also be closely linked to sensorimotor processes, which go along with the motivation and behavior to respond compassionately to another person's feelings. There is growing evidence for local plastic change in the structure of the healthy adult human brain in response to environmental demands or intrinsic factors. Here we have investigated changes in brain structure resulting from or predisposing to empathy. Structural MRI data of 101 healthy adult females was analyzed. Empathy in fictitious as well as real-life situations was assessed using a validated self-evaluation measure. Furthermore, empathy-related structural effects were also put into the context of a functional map of the anterior insular cortex (AIC) determined by activation likelihood estimate (ALE) meta-analysis of previous functional imaging studies. We found that gray matter (GM) density in the left dorsal AIC correlates with empathy and that this area overlaps with the domain general region (DGR) of the anterior insula that is situated in-between functional systems involved in emotion-cognition, pain, and motor tasks as determined by our meta-analysis. Thus, we propose that this insular region where we find structural differences depending on individual empathy may play a crucial role in modulating the efficiency of neural integration underlying emotional, cognitive, and sensorimotor information which is essential for global empathy.
Keywords: auditory perception; emotion; individual differences; language; pain; sensorimotor integration; social neuroscience; voxel-based morphometry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Domain-general and domain-preferential neural correlates underlying empathy towards physical pain, emotional situation and emotional faces: An ALE meta-analysis.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Feb 3;137:107286. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107286. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 31786222
-
Functional organization of the human anterior insular cortex.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Jun 26;457(2):66-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.101. Epub 2009 Apr 5. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19429164
-
Individual differences in local gray matter density are associated with differences in affective and cognitive empathy.Neuroimage. 2015 Aug 15;117:305-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.038. Epub 2015 May 22. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 26008886
-
Neural correlates of theory of mind and empathy in schizophrenia: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis.J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Jan;120:163-174. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.10.018. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Psychiatr Res. 2020. PMID: 31689587 Review.
-
Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain.Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):2492-502. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.014. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20946964 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural circuit disruptions of eye gaze processing in autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis.Schizophr Res. 2024 Feb;264:298-313. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2023.12.003. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Schizophr Res. 2024. PMID: 38215566 Free PMC article.
-
Association of regional gray matter volumes in the brain with disruptive behavior disorders in male and female children.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Dec 23;7:252-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.012. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25610787 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Amygdala in Environmental Sensitivity to Infant Crying.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 25;11(8):e0161181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161181. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27560361 Free PMC article.
-
Insula and somatosensory cortical myelination and iron markers underlie individual differences in empathy.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 3;7:43316. doi: 10.1038/srep43316. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28256532 Free PMC article.
-
Trait compassion is associated with the neural substrate of empathy.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017 Oct;17(5):1018-1027. doi: 10.3758/s13415-017-0529-5. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28667540
References
-
- Baron-Cohen S., Wheelwright S. (2004). The empathy quotient: an investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 34, 163–175 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

