The safety and short-term efficacy of aliskiren in the treatment of immunoglobulin a nephropathy--a randomized cross-over study
- PMID: 23675422
- PMCID: PMC3651209
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062736
The safety and short-term efficacy of aliskiren in the treatment of immunoglobulin a nephropathy--a randomized cross-over study
Abstract
Background: Laboratory research and previous study suggest that aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, has anti-proteinuric effects. We conducted a randomized crossover study to evaluate the anti-proteinuric effect of aliskiren in patients with immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy.
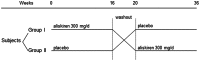
Methods: We studied 22 patients with biopsy-proven IgA nephropathy and persistent proteinuria despite angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). Patients were randomized to either oral aliskiren 300 mg/day or placebo for 16 weeks and then crossed over to the other treatment arm after a washout period. Proteinuria, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), blood pressure, and serum potassium were monitored.
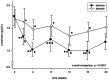
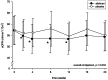
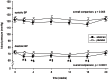
Results: After aliskiren treatment, there was a significant reduction in proteinuria in 4 weeks (1.76±0.95 to 1.03±0.69 g:g-Cr, p<0.0001), which remained at a low level throughout the treatment period. There was a significant difference in proteinuria between the aliskiren and placebo groups from 4 to 16 weeks after treatment (p<0.01 for all comparisons). After aliskiren treatment, there were modest but statistically significant reductions in eGFR (57.2±29.1 to 54.8±29.3 ml/min/1.73 m(2), p = 0.013) and diastolic blood pressure (72.6±12.3 to 66.2±11.2 mmHg, p<0.0001). None of the patient developed severe hyperkalemia (serum potassium ≥6.0 mmol/l) during the study period.
Conclusions: Aliskiren has anti-proteinuric effect in patients with IgA nephropathy and persistent proteinuria despite ACE inhibitor or ARB. Further studies are needed to confirm the renal protecting effect of direct renin inhibition in chronic proteinuric kidney diseases.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00870493.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
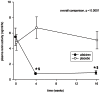
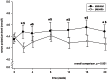
References
-
- D’Amico G (1987) The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med 245: 709–727. - PubMed
-
- Li PKT, Ho KKL, Szeto CC, Yu LM, Lai FM (2002) Prognostic Indicators of IgA Nephropathy in the Chinese – Clinical and Pathological Perspectives. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17: 64–69. - PubMed
-
- Haas M (1997) Histologic subclassification of IgA nephropathy: a clinico-pathologic study of 244 cases. Am J Kidney Dis 29: 829–842. - PubMed
-
- Maschio G, Cagnoli L, Claroni F, Fusaroli M, Rugiu C, et al. (1994) ACE inhibition reduce proteinuria in normotensive patients with IgA nephropathy: a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 9: 265–269. - PubMed
-
- Russo D, Pisani A, Balletta MM, De Nicola L, Savino FA, et al. (1999) Additive anti-proteinuric effect of converting enzyme inhibitor and losartan in normotensive patients with IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 33: 851–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

