Integrating murine gene expression studies to understand obstructive lung disease due to chronic inhaled endotoxin
- PMID: 23675439
- PMCID: PMC3652821
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062910
Integrating murine gene expression studies to understand obstructive lung disease due to chronic inhaled endotoxin
Abstract
Rationale: Endotoxin is a near ubiquitous environmental exposure that that has been associated with both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These obstructive lung diseases have a complex pathophysiology, making them difficult to study comprehensively in the context of endotoxin. Genome-wide gene expression studies have been used to identify a molecular snapshot of the response to environmental exposures. Identification of differentially expressed genes shared across all published murine models of chronic inhaled endotoxin will provide insight into the biology underlying endotoxin-associated lung disease.
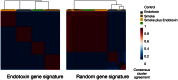
Methods: We identified three published murine models with gene expression profiling after repeated low-dose inhaled endotoxin. All array data from these experiments were re-analyzed, annotated consistently, and tested for shared genes found to be differentially expressed. Additional functional comparison was conducted by testing for significant enrichment of differentially expressed genes in known pathways. The importance of this gene signature in smoking-related lung disease was assessed using hierarchical clustering in an independent experiment where mice were exposed to endotoxin, smoke, and endotoxin plus smoke.
Results: A 101-gene signature was detected in three murine models, more than expected by chance. The three model systems exhibit additional similarity beyond shared genes when compared at the pathway level, with increasing enrichment of inflammatory pathways associated with longer duration of endotoxin exposure. Genes and pathways important in both asthma and COPD were shared across all endotoxin models. Mice exposed to endotoxin, smoke, and smoke plus endotoxin were accurately classified with the endotoxin gene signature.
Conclusions: Despite the differences in laboratory, duration of exposure, and strain of mouse used in three experimental models of chronic inhaled endotoxin, surprising similarities in gene expression were observed. The endotoxin component of tobacco smoke may play an important role in disease development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Overlap of Lung Tissue Transcriptome of Smoke Exposed Mice with Human Smoking and COPD.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 8;8(1):11881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30313-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30089872 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Lung Tissue from Cigarette Smoke-Induced Emphysema Murine Models and Human Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Show Shared and Distinct Pathways.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017 Jul;57(1):47-58. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0328OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28248572 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic endotoxin exposure produces airflow obstruction and lung dendritic cell expansion.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;47(2):209-17. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0447OC. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22517795 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and gene transcription in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: antioxidant therapeutic targets.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002 Sep;1(3):291-315. doi: 10.2174/1568010023344607. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002. PMID: 14561194 Review.
-
Translating the COPD transcriptome: insights into pathogenesis and tools for clinical management.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008 Dec 1;5(8):834-41. doi: 10.1513/pats.200807-074TH. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. PMID: 19017738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liebers V, Raulf-Heimsoth M, Brüning T (2008) Health effects due to endotoxin inhalation (review). Arch Toxicol 82: 203–210. - PubMed
-
- Braun-Fahrlander C, Riedler J, Herz U, Eder W, Waser M, et al. (2002) Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N Engl J Med 347: 869–877. - PubMed
-
- Salvi SS, Barnes PJ (2009) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in non-smokers. Lancet 374: 733–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

