A soft coral-derived compound, 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate suppresses inflammatory response and bone destruction in adjuvant-induced arthritis
- PMID: 23675440
- PMCID: PMC3652811
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062926
A soft coral-derived compound, 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate suppresses inflammatory response and bone destruction in adjuvant-induced arthritis
Abstract
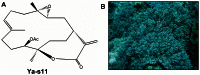
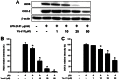
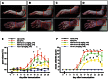
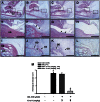
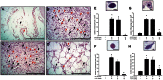
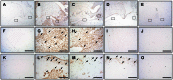
In recent years, a significant number of metabolites with potent anti-inflammatory properties have been discovered from marine organisms, and several of these compounds are now under clinical trials. In the present study, we isolated 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate (Ya-s11), a cembrane-type compound with anti-inflammatory effects, from the Formosa soft coral Sinularia querciformis. Preliminary screening revealed that Ya-s11 significantly inhibited the expression of the proinflammatory proteins induced nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages. We also examined the therapeutic effects of Ya-s11 on adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in female Lewis rats, which demonstrate features similar to human rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Animal experiments revealed that Ya-s11 (subcutaneously 9 mg/kg once every 2 days from day 7 to day 28 postimmunization) significantly inhibited AIA characteristics. Moreover, Ya-s11 also attenuated protein expression of cathepsin K, matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9), tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in ankle tissues of AIA-rats. Based on its attenuation of the expression of proinflammatory proteins and disease progression in AIA rats, the marine-derived compound Ya-s11 may serve as a useful therapeutic agent for the treatment of RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Excavatolide B Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis through the Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis.Mar Drugs. 2017 Jan 6;15(1):9. doi: 10.3390/md15010009. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28067799 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of progressive joint destruction in adjuvant induced arthritis in rats by a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, FR217840.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Jan 31;508(1-3):239-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.12.014. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15680277
-
Downregulation of inflammatory mediators and pro-inflammatory cytokines by alkaloids of Jeevaneeya rasayana in adjuvant-induced arthritis.Immunol Invest. 2015;44(1):70-87. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2014.936937. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Immunol Invest. 2015. PMID: 25058430
-
Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia querciformis and Sinularia granosa.J Nat Prod. 2008 Oct;71(10):1754-9. doi: 10.1021/np8003563. Epub 2008 Oct 3. J Nat Prod. 2008. PMID: 18831569
-
Low dose of propranolol down-modulates bone resorption by inhibiting inflammation and osteoclast differentiation.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(7):2140-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01686.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21950592 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early arthritis induces disturbances at bone nanostructural level reflected in decreased tissue hardness in an animal model of arthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 9;13(1):e0190920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190920. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29315314 Free PMC article.
-
The application and sustainable development of coral in traditional medicine and its chemical composition, pharmacology, toxicology, and clinical research.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1230608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1230608. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Natural Products from Indonesian Waters.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jun 19;17(6):364. doi: 10.3390/md17060364. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31248122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jun 14;16(6):210. doi: 10.3390/md16060210. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29903990 Free PMC article.
-
Arthritis induces early bone high turnover, structural degradation and mechanical weakness.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 24;10(1):e0117100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117100. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25617902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noguchi M, Kimoto A, Kobayashi S, Yoshino T, Miyata K, et al. (2005) Effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on the pathophysiology of adjuvant arthritis in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 513: 229–235. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423: 356–361. - PubMed
-
- Scott DL, Smith C, Kingsley G (2003) Joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis: an updated systematic review. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21: 20–27. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita A, Yonemitsu Y, Okano S, Nakagawa K, Nakashima Y, et al. (2002) Fibroblast growth factor-2 determines severity of joint disease in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J Immunol 168: 450–457. - PubMed
-
- Noss EH, Brenner MB (2008) The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 223: 252–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

