Structural and functional connectivity changes in the brain associated with shyness but not with social anxiety
- PMID: 23675458
- PMCID: PMC3651210
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063151
Structural and functional connectivity changes in the brain associated with shyness but not with social anxiety
Abstract
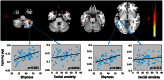
Shyness and social anxiety are correlated to some extent and both are associated with hyper-responsivity to social stimuli in the frontal cortex and limbic system. However to date no studies have investigated whether common structural and functional connectivity differences in the brain may contribute to these traits. We addressed this issue in a cohort of 61 healthy adult subjects. Subjects were first assessed for their levels of shyness (Cheek and Buss Shyness scale) and social anxiety (Liebowitz Social Anxiety scale) and trait anxiety. They were then given MRI scans and voxel-based morphometry and seed-based, resting-state functional connectivity analysis investigated correlations with shyness and anxiety scores. Shyness scores were positively correlated with gray matter density in the cerebellum, bilateral superior temporal gyri and parahippocampal gyri and right insula. Functional connectivity correlations with shyness were found between the superior temporal gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus and the frontal gyri, between the insula and precentral gyrus and inferior parietal lobule, and between the cerebellum and precuneus. Additional correlations were found for amygdala connectivity with the medial frontal gyrus, superior frontal gyrus and inferior parietal lobule, despite the absence of any structural correlation. By contrast no structural or functional connectivity measures correlated with social or trait anxiety. Our findings show that shyness is specifically associated with structural and functional connectivity changes in cortical and limbic regions involved with processing social stimuli. These associations are not found with social or trait anxiety in healthy subjects despite some behavioral correlations with shyness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Henderson HA (2010) Electrophysiological correlates of cognitive control and the regulation of shyness in children. Dev Neuropsychol 35: 177–193. - PubMed
-
- Zimbardo PG (1977) Shyness: What is it and what to do about it. New York: Symphony.
-
- Battaglia M, Ogliari A, Zanoni A, Citterio A, Pozzoli U, et al. (2005) Influence of the serotonin transporter promoter gene and shyness on children's cerebral responses to facial expressions. Archives of General Psychiatry 62: 85–94. - PubMed
-
- Cheek JM, Melchior LA (1990) Shyness, self-esteem, and self-consciousness. In H. Leitenberg (Ed.), Handbook of social and evaluation anxiety (pp. 47–82). New York: Plenum.
-
- Dennissen JJ, Asendorpf JB, van Aken MA (2008) Childhood personality predicts long-term trajectories of shyness and aggressiveness in the context of demographic transitions in emerging adulthood. J Pers 76: 67–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

