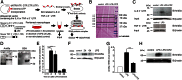
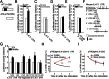
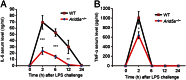
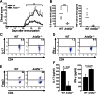
Arid5a controls IL-6 mRNA stability, which contributes to elevation of IL-6 level in vivo
- PMID: 23676272
- PMCID: PMC3677444
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1307419110
Arid5a controls IL-6 mRNA stability, which contributes to elevation of IL-6 level in vivo
Abstract
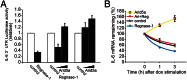
Posttranscriptional regulation of IL-6 has been largely uncharacterized, with the exception of the ribonuclease Regnase-1, which prevents autoimmunity by destabilizing IL-6 mRNA. Here, we identified AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5A (Arid5a) as a unique RNA binding protein, which stabilizes IL-6 but not TNF-α mRNA through binding to the 3' untranslated region of IL-6 mRNA. Arid5a was enhanced in macrophages in response to LPS, IL-1β, and IL-6. Arid5a deficiency inhibited elevation of IL-6 serum level in LPS-treated mice and suppressed IL-6 levels and the development of T(H)17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Importantly, Arid5a inhibited the destabilizing effect of Regnase-1 on IL-6 mRNA. These results indicate that Arid5a plays an important role in promotion of inflammatory processes and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: RNA-protein complex; immune regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6: From basic science to medicine—40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF, Finotto S. IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011;22(2):83–89. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. Immunotherapeutic implication of IL-6 blockade. Immunotherapy. 2012;4(1):87–105. - PubMed
-
- Mima T, Nishimoto N. Clinical value of blocking IL-6 receptor. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009;21(3):224–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

