Molecular signatures in skin associated with clinical improvement during mycophenolate treatment in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 23677167
- PMCID: PMC3714324
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.130
Molecular signatures in skin associated with clinical improvement during mycophenolate treatment in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Heterogeneity in systemic sclerosis (SSc) confounds clinical trials. We previously identified "intrinsic" gene expression subsets by analysis of SSc skin. Here we test the hypotheses that skin gene expression signatures including intrinsic subset are associated with modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS) improvement during mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) treatment. Gene expression and intrinsic subset assignment were measured in 12 SSc patients' biopsies and 10 controls at baseline, and from serial biopsies of 1 cyclophosphamide-treated patient and 9 MMF-treated patients. Gene expression changes during treatment were determined using paired t-tests corrected for multiple hypothesis testing. MRSS improved in four of seven MMF-treated patients classified as the inflammatory intrinsic subset. Three patients without MRSS improvement were classified as normal-like or fibroproliferative intrinsic subsets. A total of 321 genes (false discovery rate (FDR)<5%) were differentially expressed at baseline between patients with and without MRSS improvement during treatment. The expression of 571 genes (FDR<10%) changed between pre- and post-MMF treatment biopsies for patients showing MRSS improvement. Gene expression changes in skin are only seen in patients with MRSS improvement. Baseline gene expression in skin, including intrinsic subset assignment, may identify SSc patients whose MRSS will improve during MMF treatment, suggesting that gene expression in skin may allow targeted treatment in SSc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

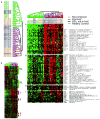
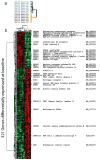

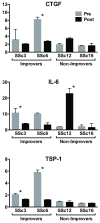
References
-
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:581–90. - PubMed
-
- Dennis G, Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, et al. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome biology. 2003;4:P3. - PubMed
-
- Derk CT, Grace E, Shenin M, Naik M, Schulz S, Xiong W. A prospective open-label study of mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of diffuse systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:1595–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R25CA134286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042309/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50AR060780/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 610-532-800-6001417/PHS HHS/United States
- R25 CA134286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051089/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR055063/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR064464/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR048098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD055884/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR48098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR060780/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR059763/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

