Updating RNA-Seq analyses after re-annotation
- PMID: 23677943
- PMCID: PMC3694665
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt197
Updating RNA-Seq analyses after re-annotation
Abstract
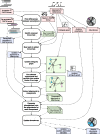
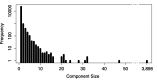
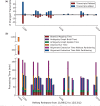
The estimation of isoform abundances from RNA-Seq data requires a time-intensive step of mapping reads to either an assembled or previously annotated transcriptome, followed by an optimization procedure for deconvolution of multi-mapping reads. These procedures are essential for downstream analysis such as differential expression. In cases where it is desirable to adjust the underlying annotation, for example, on the discovery of novel isoforms or errors in existing annotations, current pipelines must be rerun from scratch. This makes it difficult to update abundance estimates after re-annotation, or to explore the effect of changes in the transcriptome on analyses. We present a novel efficient algorithm for updating abundance estimates from RNA-Seq experiments on re-annotation that does not require re-analysis of the entire dataset. Our approach is based on a fast partitioning algorithm for identifying transcripts whose abundances may depend on the added or deleted isoforms, and on a fast follow-up approach to re-estimating abundances for all transcripts. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods by showing how to synchronize RNA-Seq abundance estimates with the daily RefSeq incremental updates. Thus, we provide a practical approach to maintaining relevant databases of RNA-Seq derived abundance estimates even as annotations are being constantly revised.
Availability and implementation: Our methods are implemented in software called ReXpress and are freely available, together with source code, at http://bio.math.berkeley.edu/ReXpress/.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
References
-
- Asmann YW, et al. Detection of redundant fusion transcripts as biomarkers or disease-specific therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1921–1928. - PubMed
-
- Bichot CE, Siarry P, editors. Graph Partitioning. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

