Biochemical features of a catalytic antibody light chain, 22F6, prepared from human lymphocytes
- PMID: 23677996
- PMCID: PMC3707657
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454579
Biochemical features of a catalytic antibody light chain, 22F6, prepared from human lymphocytes
Abstract
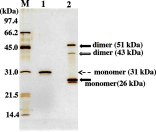
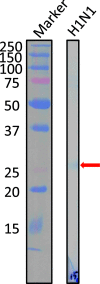
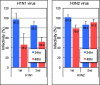
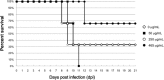
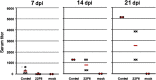
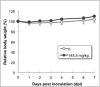
Human antibody light chains belonging to subgroup II of germ line genes were amplified by a seminested PCR technique using B-lymphocytes taken from a human adult infected with influenza virus. Each gene of the human light chains was transferred into the Escherichia coli system. The recovered light chain was highly purified using a two-step purification system. Light chain 22F6 showed interesting catalytic features. The light chain cleaved a peptide bond of synthetic peptidyl-4-methyl-coumaryl-7-amide (MCA) substrates, such as QAR-MCA and EAR-MCA, indicating amidase activity. It also hydrolyzed a phosphodiester bond of both DNA and RNA. From the analysis of amino acid sequences and molecular modeling, the 22F6 light chain possesses two kinds of active sites as amidase and nuclease in close distances. The 22F6 catalytic light chain could suppress the infection of influenza virus type A (H1N1) of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells in an in vitro assay. In addition, the catalytic light chain clearly inhibited the infection of the influenza virus of BALB/c mice via nasal administration in an in vivo assay. In the experiment, the titer in the serum of the mice coinfected with the 22F6 light chain and H1N1 virus became considerably lowered compared with that of 22F6-non-coinfected mice. Note that the catalytic light chain was prepared from human peripheral lymphocyte and plays an important role in preventing infection by influenza virus. Considering the fact that the human light chain did not show any acute toxicity for mice, our procedure developed in this study must be unique and noteworthy for developing new drugs.
Keywords: Catalytic Antibody; DNase; Enzyme Catalysis; Human Light Chain; Influenza Virus; Influenza Virus Type A; Molecular Modeling; RNA Catalysis.
Figures


References
-
- Mei S., Mody B., Eklund S. H., Paul S. (1991) Vasoactive intestinal peptide hydrolysis by antibody light chains. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 15571–15574 - PubMed
-
- Shuster A. M., Gololobov G. V., Kvashuk O. A., Bogomolova A. E., Smirnov I. V., Gabibov A. G. (1992) DNA hydrolyzing autoantibodies. Science 256, 665–667 - PubMed
-
- Hifumi E., Mitsuda Y., Ohara K., Uda T. (2002) Targeted destruction of the HIV-1 coat protein gp41 by a catalytic antibody light chain. J. Immunol. Methods 269, 283–298 - PubMed
-
- Paul S., Karle S., Planque S., Taguchi H., Salas M., Nishiyama Y., Handy B., Hunter R., Edmundson A., Hanson C. (2004) Naturally occurring proteolytic antibodies. Selective immunoglobulin M-catalyzed hydrolysis of HIV gp120. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 39611–39619 - PubMed
-
- Lacroix-Desmazes S., Moreau A., Sooryanarayana, Bonnemain C., Stieltjes N., Pashov A., Sultan Y., Hoebeke J., Kazatchkine M. D., Kaveri S. V. (1999) Catalytic activity of antibodies against factor VIII in patients with hemophilia A. Nat. Med. 5, 1044–1047 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

