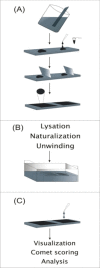
Comet assay: a method to evaluate genotoxicity of nano-drug delivery system
- PMID: 23678412
- PMCID: PMC3648950
- DOI: 10.5681/bi.2011.012
Comet assay: a method to evaluate genotoxicity of nano-drug delivery system
Abstract
Introduction: Drug delivery systems could induce cellular toxicity as side effect of nanomaterials. The mechanism of toxicity usually involves DNA damage. The comet assay or single cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) is a sensitive method for detecting strand damages in the DNA of a cell with applications in genotoxicity testing and molecular epidemiology as well as fundamental research in DNA damage and repair.
Methods: In the current study, we reviewed recent drug delivery researches related to SCGE.
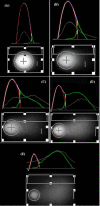
Results: We found that one preference for choosing the assay is that comet images may result from apoptosis-mediated nuclear fragmentation. This method has been widely used over the last decade in several different areas. Overall cells, such as cultured cells are embedded in agarose on a microscope slide, lysed with detergent, and treated with high salt. Nucleoids are supercoiled DNA form. When the slide is faced to alkaline electrophoresis any breakages present in the DNA cause the supercoiling to relax locally and loops of DNA extend toward the anode as a ''comet tail''.
Conclusion: This article provides a relatively comprehensive review upon potentiality of the comet assay for assessment of DNA damage and accordingly it can be used as an informative platform in genotoxicity studies of drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Comet Assay; DNA; Drug Delivery; Genotoxicity; Nanoparticle; Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis.
Similar articles
-
The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: principles, applications, and limitations.Mol Biotechnol. 2004 Mar;26(3):249-61. doi: 10.1385/MB:26:3:249. Mol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15004294 Review.
-
Increasing the resolution of the comet assay using fluorescent in situ hybridization--a review.Mutagenesis. 2009 Sep;24(5):383-9. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gep021. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Mutagenesis. 2009. PMID: 19535362 Review.
-
Genotoxicity of environmental agents assessed by the alkaline comet assay.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96 Suppl 1:1-42. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15859009 Review.
-
The comet assay: a sensitive genotoxicity test for the detection of DNA damage and repair.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;314:275-86. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-973-7:275. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16673888
-
Sperm DNA damage measured by comet assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;927:137-46. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-038-0_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22992910
Cited by
-
Physico-Chemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Thermosensitive Chitosan Lactate and Chitosan Chloride Hydrogels Developed for Tissue Engineering Application.J Funct Biomater. 2021 May 20;12(2):37. doi: 10.3390/jfb12020037. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34065271 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity Assessment of Metal-Based Nanocomposites Applied in Drug Delivery.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 1;14(21):6551. doi: 10.3390/ma14216551. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34772074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Chrysotile Asbestos in MRC5 Cell Line.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 12;13(11):1599. doi: 10.3390/jpm13111599. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38003914 Free PMC article.
-
Sclareol Inhibits Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Accumulation and Induces Apoptosis in Hypoxic Cancer Cells.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 May;12(3):593-602. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.062. Epub 2021 Jul 4. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35935045 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating nanobiomaterial-induced DNA strand breaks using the alkaline comet assay.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Sep;12(9):2243-2258. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01178-7. Epub 2022 May 25. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35612707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arayne Ms, Sultana N and Qureshi F . 2007 Review: nanoparticles in delivery of cardiovascular drugs. Pak J Pharm Sci, 20(4), 340-8 - PubMed
-
- Aschberger K, Johnston Hj, Stone V, Aitken Rj, Tran Cl, Hankin Sm, et al.2010 Review of fullerene toxicity and exposure--appraisal of a human health risk assessment, based on open literature. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol, 58(3), 455-73 - PubMed
-
- Barnes Ca, Elsaesser A, Arkusz J, Smok A, Palus J, Lesniak A, et al.2008 Reproducible comet assay of amorphous silica nanoparticles detects no genotoxicity. Nano Lett, 8(9), 3069-74 - PubMed
-
- Beaux Mf, Mcilroy Dn and Gustin Ke . 2008 Utilization of solid nanomaterials for drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv, 5(7), 725-35 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources