Rosuvastatin does not affect fasting glucose, insulin resistance, or adiponectin in patients with mild to moderate hypertension
- PMID: 23678475
- PMCID: PMC3651984
- DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2013.49.1.31
Rosuvastatin does not affect fasting glucose, insulin resistance, or adiponectin in patients with mild to moderate hypertension
Abstract
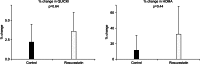
The effects of statins on insulin resistance and new-onset diabetes are unclear. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of rosuvastatin on insulin resistance and adiponectin in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. In a randomized, prospective, single-blind study, 53 hypertensive patients were randomly assigned to the control group (n=26) or the rosuvastatin (20 mg once daily) group (n=27) during an 8-week treatment period. Both groups showed significant improvements in systolic blood pressure and flow-mediated dilation (FMD) after 8 weeks of treatment. Rosuvastatin treatment improved total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. The control and rosuvastatin treatment groups did not differ significantly in the change in HbA1c (3.0±10.1% vs. -1.3±12.7%; p=0.33), fasting glucose (-1.3±18.0% vs. 2.5±24.1%; p=0.69), or fasting insulin levels (5.2±70.5% vs. 22.6±133.2%; p=0.27) from baseline. Furthermore, the control and rosuvastatin treatment groups did not differ significantly in the change in the QUICKI insulin sensitivity index (mean change, 2.2±11.6% vs. 3.6±11.9%; p=0.64) or the HOMA index (11.6±94.9% vs. 32.4±176.7%; p=0.44). The plasma adiponectin level increased significantly in the rosuvastatin treatment group (p=0.046), but did not differ significantly from that in the control group (mean change, 23.2±28.4% vs. 23.1±27.6%; p=0.36). Eight weeks of rosuvastatin (20 mg) therapy resulted in no significant improvement or deterioration in fasting glucose levels, insulin resistance, or adiponectin levels in patients with mild to moderate hypertension.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Blood glucose; Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors; Insulin resistance.
Figures



References
-
- Han SH, Quon MJ, Koh KK. Reciprocal relationships between abnormal metabolic parameters and endothelial dysfunction. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007;18:58–65. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers J, MacMahon S, Mancia G, Whitworth J, Beilin L, Hansson L, et al. 1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of hypertension. Guidelines sub-committee of the World Health Organization. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1999;21:1009–1060. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Jr, Kastelein JJ, et al. JUPITER Study Group. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2195–2207. - PubMed
-
- Koh KK. Effects of statins on vascular wall: vasomotor function, inflammation, and plaque stability. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;47:648–657. - PubMed
-
- Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Ahn JY, Jin DK, Kim HS, et al. Vascular and metabolic effects of combined therapy with ramipril and simvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hypertension. 2005;45:1088–1093. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

