N-Aroyl indole thiobarbituric acids as inhibitors of DNA repair and replication stress response polymerases
- PMID: 23679919
- PMCID: PMC3746001
- DOI: 10.1021/cb400305r
N-Aroyl indole thiobarbituric acids as inhibitors of DNA repair and replication stress response polymerases
Abstract
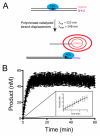
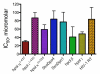
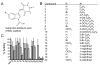
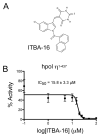
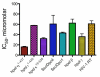
Using a robust and quantitative assay, we have identified a novel class of DNA polymerase inhibitors that exhibits some specificity against an enzyme involved in resistance to anti-cancer drugs, namely, human DNA polymerase eta (hpol η). In our initial screen, we identified the indole thiobarbituric acid (ITBA) derivative 5-((1-(2-bromobenzoyl)-5-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-2-thioxodihydropyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-dione (ITBA-12) as an inhibitor of the Y-family DNA member hpol η, an enzyme that has been associated with increased resistance to cisplatin and doxorubicin treatments. An additional seven DNA polymerases from different subfamilies were tested for inhibition by ITBA-12. Hpol η was the most potently inhibited enzyme (30 ± 3 μM), with hpol β, hpol γ, and hpol κ exhibiting comparable but higher IC50 values of 41 ± 24, 49 ± 6, and 59 ± 11 μM, respectively. The other polymerases tested had IC50 values closer to 80 μM. Steady-state kinetic analysis was used to investigate the mechanism of polymerase inhibition by ITBA-12. Based on changes in the Michaelis constant, it was determined that ITBA-12 acts as an allosteric (or partial) competitive inhibitor of dNTP binding. The parent ITBA scaffold was modified to produce 20 derivatives and establish structure-activity relationships by testing for inhibition of hpol η. Two compounds with N-naphthoyl Ar-substituents, ITBA-16 and ITBA-19, were both found to have improved potency against hpol η with IC50 values of 16 ± 3 μM and 17 ± 3 μM, respectively. Moreover, the specificity of ITBA-16 was improved relative to that of ITBA-12. The presence of a chloro substituent at position 5 on the indole ring appears to be crucial for effective inhibition of hpol η, with the indole N-1-naphthoyl and N-2-naphthoyl analogues being the most potent inhibitors of hpol η. These results provide a framework from which second-generation ITBA derivatives may be developed against specialized polymerases that are involved in mechanisms of radio- and chemo-resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Human DNA Polymerase η Potentiates the Effects of Cisplatin in Tumor Cells.Biochemistry. 2018 Feb 20;57(7):1262-1273. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01176. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29345908 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Human DNA Polymerases Eta and Kappa by Indole-Derived Molecules Occurs through Distinct Mechanisms.ACS Chem Biol. 2019 Jun 21;14(6):1337-1351. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00304. Epub 2019 May 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31082191 Free PMC article.
-
N-Naphthoyl-substituted indole thio-barbituric acid analogs inhibit the helicase activity of the hepatitis C virus NS3.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Feb 1;29(3):430-434. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.12.026. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 30578035 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerase eta: A potential pharmacological target for cancer therapy.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jun;236(6):4106-4120. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30155. Epub 2020 Nov 13. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33184862 Review.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of APE1 DNA repair function: an overview.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;5(1):14-35. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22122462 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and anti-proliferative activity of aromatic substituted 5-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione analogs against human tumor cell lines.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jan 15;24(2):601-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.013. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24361000 Free PMC article.
-
A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Human DNA Polymerase η Potentiates the Effects of Cisplatin in Tumor Cells.Biochemistry. 2018 Feb 20;57(7):1262-1273. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01176. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29345908 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage Tolerance Pathways in Human Cells: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 7;11:822500. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.822500. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35198436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translesion synthesis inhibitors as a new class of cancer chemotherapeutics.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021 Jan;30(1):13-24. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1850692. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33179552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging the replication stress response to optimize cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Jan;23(1):6-24. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00518-6. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36323800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cha RS, Kleckner N. ATR homolog Mec1 promotes fork progression, thus averting breaks in replication slow zones. Science. 2002;297:602–606. - PubMed
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Shultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. 2nd ed ASM Press; Washington, D.C.: 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

