Microneedles for intradermal and transdermal drug delivery
- PMID: 23680534
- PMCID: PMC4119996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.05.005
Microneedles for intradermal and transdermal drug delivery
Abstract
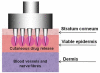
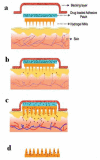
The formidable barrier properties of the uppermost layer of the skin, the stratum corneum, impose significant limitations for successful systemic delivery of broad range of therapeutic molecules particularly macromolecules and genetic material. Microneedle (MN) has been proposed as a strategy to breach the stratum corneum barrier function in order to facilitate effective transport of molecules across the skin. This strategy involves use of micron sized needles fabricated of different materials and geometries to create transient aqueous conduits across the skin. MN, alone or with other enhancing strategies, has been demonstrated to dramatically enhance the skin permeability of numerous therapeutic molecules including biopharmaceuticals either in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo experiments. This suggested the promising use of MN technology for various possible clinical applications such as insulin delivery, transcutaneous immunisations and cutaneous gene delivery. MN has been proved as minimally invasive and painless in human subjects. This review article focuses on recent and future developments for MN technology including the latest type of MN design, challenges and strategies in MNs development as well as potential safety aspects based on comprehensive literature review pertaining to MN studies to date.
Keywords: Drug monitoring; Hydrogel-forming; Microneedle; Safety; Transdermal drug delivery; Vaccination.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aoyagi S, Izumi H, Fukuda M. Biodegradable polymer needle with various tip angles and consideration on insertion mechanism of mosquito’s proboscis. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical. 2008;143(1):20–28.
-
- Aoyagi S, Izumi H, Isono Y, et al. Laser fabrication of high aspect ratio thin holes on biodegradable polymer and its application to a microneedle. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical. 2007;139(1-2):293–302.
-
- Bal SM, Caussin J, Pavel S, et al. In vivo assessment of safety of microneedle arrays in human skin. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2008;35(3):193–202. - PubMed
-
- Banga AK. Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins: Formulation, Processing and Delivery Systems. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group; Boca Raton: 2006.
Websites
-
- [Accessed on 19 March 2013];Dermaroller®. http://www.genuinedermaroller.co.uk.
-
- [Accessed on 19 March 2013];Skin Permeation Enhancer (SPE™) Nanopin. http://www.nanomed-skincare.com/en/core_tech.asp.
-
- [Accessed on 19 March 2013];Derma-Q and Mi-roll Micro Needle Roller. http://www.dermaneedle.com/
-
- [Accessed on 27 March 2013];Dermaroller®. http://www.dermaroller.com.
-
- [Accessed on 27 March 2013];Beckton-Dickinson’ Soluvia®. http://www.bd.com.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

