How plants LINC the SUN to KASH
- PMID: 23680964
- PMCID: PMC3720751
- DOI: 10.4161/nucl.24088
How plants LINC the SUN to KASH
Abstract
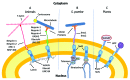
Linkers of the nucleoskeleton to the cytoskeleton (LINC) complexes formed by SUN and KASH proteins are conserved eukaryotic protein complexes that bridge the nuclear envelope (NE) via protein-protein interactions in the NE lumen. Revealed by opisthokont studies, LINC complexes are key players in multiple cellular processes, such as nuclear and chromosomal positioning and nuclear shape determination, which in turn influence the generation of gametes and several aspects of development. Although comparable processes have long been known in plants, the first plant nuclear envelope bridging complexes were only recently identified. WPP domain-interacting proteins at the outer NE have little homology to known opisthokont KASH proteins, but form complexes with SUN proteins at the inner NE that have plant-specific properties and functions. In this review, we will address the importance of LINC complex-regulated processes, describe the plant NE bridging complexes and compare them to opisthokont LINC complexes.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; KASH; LINC complex; SUN; nuclear envelope; plant.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
