Automated alerting and recommendations for the management of patients with preexisting hypoxia and potential acute lung injury: a pilot study
- PMID: 23681144
- PMCID: PMC3813292
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182987af4
Automated alerting and recommendations for the management of patients with preexisting hypoxia and potential acute lung injury: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is associated with high mortality. Low tidal volume (Vt) ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in ALI patients in the intensive care unit. Anesthesiologists do not routinely provide lung-protective ventilation strategies to patients with ALI in the operating room. The authors hypothesized that an alert, recommending lung-protective ventilation regarding patients with potential ALI, would result in lower Vt administration.
Methods: The authors conducted a randomized controlled trial on anesthesia providers caring for patients with potential ALI. Patients with an average or last collected ratio of partial pressure of arterial oxygen to inspired fraction of oxygen less than 300 were randomized to providers being sent an alert with a recommended Vt of 6 cc/kg predicted body weight or conventional care. Primary outcomes were Vt/kg predicted body weight administered to patients. Secondary outcomes included ventilator parameters, length of postoperative ventilation, and death.
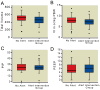
Results: The primary outcome was a clinically significant reduction in mean Vt from 508-458 cc (P = 0.033), with a reduction in Vt when measured in cc/kg predicted body weight from 8 to 7.2 cc/kg predicted body weight (P = 0.040). There were no statistically significant changes in other outcomes or adverse events associated with either arm.
Conclusions: Automated alerts generated for patients at risk of having ALI resulted in a statistically significant reduction in Vt administered when compared with a control group. Further research is required to determine whether a reduction in Vt results in decreased mortality and/or postoperative duration of mechanical ventilation.
References
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS: Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149:818–24. - PubMed
-
- Hudson LD, Milberg JA, Anardi D, Maunder RJ. Clinical risks for development of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–48. - PubMed
-
- Bersten AD, Edibam C, Hunt T, Moran J. Incidence and mortality of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in three Australian States. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:443–8. - PubMed
-
- Goss CH, Brower RG, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD. Incidence of acute lung injury in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1607–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical