SIRT1 activation enhances HDAC inhibition-mediated upregulation of GADD45G by repressing the binding of NF-κB/STAT3 complex to its promoter in malignant lymphoid cells
- PMID: 23681230
- PMCID: PMC3674366
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.159
SIRT1 activation enhances HDAC inhibition-mediated upregulation of GADD45G by repressing the binding of NF-κB/STAT3 complex to its promoter in malignant lymphoid cells
Abstract
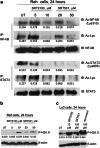
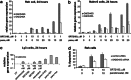
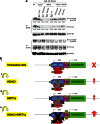
We explored the activity of SIRT1 activators (SRT501 and SRT2183) alone and in combination with panobinostat in a panel of malignant lymphoid cell lines in terms of biological and gene expression responses. SRT501 and SRT2183 induced growth arrest and apoptosis, concomitant with deacetylation of STAT3 and NF-κB, and reduction of c-Myc protein levels. PCR arrays revealed that SRT2183 leads to increased mRNA levels of pro-apoptosis and DNA-damage-response genes, accompanied by accumulation of phospho-H2A.X levels. Next, ChIP assays revealed that SRT2183 reduces the DNA-binding activity of both NF-κB and STAT3 to the promoter of GADD45G, which is one of the most upregulated genes following SRT2183 treatment. Combination of SRT2183 with panobinostat enhanced the anti-growth and anti-survival effects mediated by either compound alone. Quantitative-PCR confirmed that the panobinostat in combination with SRT2183, SRT501 or resveratrol leads to greater upregulation of GADD45G than any of the single agents. Panobinostat plus SRT2183 in combination showed greater inhibition of c-Myc protein levels and phosphorylation of H2A.X, and increased acetylation of p53. Furthermore, EMSA revealed that NF-κB binds directly to the GADD45G promoter, while STAT3 binds indirectly in complexes with NF-κB. In addition, the binding of NF-κB/STAT3 complexes to the GADD45G promoter is inhibited following panobinostat, SRT501 or resveratrol treatment. Moreover, the combination of panobinostat with SRT2183, SRT501 or resveratrol induces a greater binding repression than either agent alone. These data suggest that STAT3 is a corepressor with NF-κB of the GADD45G gene and provides in vitro proof-of-concept for the combination of HDACi with SIRT1 activators as a potential new therapeutic strategy in lymphoid malignancies.
Figures





References
-
- Stimson L, Wood V, Khan O, Fotheringham S, La Thangue NB. HDAC inhibitor-based therapies and haematological malignancy. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1293–1302. - PubMed
-
- Frye RA. Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: Sir2-like proteins (sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;260:273–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

