Neuropeptide Y receptors activation protects rat retinal neural cells against necrotic and apoptotic cell death induced by glutamate
- PMID: 23681231
- PMCID: PMC3674367
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.160
Neuropeptide Y receptors activation protects rat retinal neural cells against necrotic and apoptotic cell death induced by glutamate
Abstract
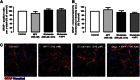
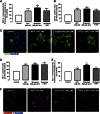
It has been claimed that glutamate excitotoxicity might have a role in the pathogenesis of several retinal degenerative diseases, including glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) has neuroprotective properties against excitotoxicity in the hippocampus, through the activation of Y1, Y2 and/or Y5 receptors. The principal objective of this study is to investigate the potential protective role of NPY against glutamate-induced toxicity in rat retinal cells (in vitro and in an animal model), unraveling the NPY receptors and intracellular mechanisms involved. Rat retinal neural cell cultures were prepared from newborn Wistar rats (P3-P5) and exposed to glutamate (500 μM) for 24 h. Necrotic cell death was evaluated by propidium iodide (PI) assay and apoptotic cell death using TUNEL and caspase-3 assays. The cell types present in culture were identified by immunocytochemistry. The involvement of NPY receptors was assessed using selective agonists and antagonists. Pre-treatment of cells with NPY (100 nM) inhibited both necrotic cell death (PI-positive cells) and apoptotic cell death (TUNEL-positive cells and caspase 3-positive cells) triggered by glutamate, with the neurons being the cells most strongly affected. The activation of NPY Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptors inhibited necrotic cell death, while apoptotic cell death was only prevented by the activation of NPY Y5 receptor. Moreover, NPY neuroprotective effect was mediated by the activation of PKA and p38K. In the animal model, NPY (2.35 nmol) was intravitreally injected 2 h before glutamate (500 nmol) injection into the vitreous. The protective role of NPY was assessed 24 h after glutamate (or saline) injection by TUNEL assay and Brn3a (marker of ganglion cells) immunohistochemistry. NPY inhibited the increase in the number of TUNEL-positive cells and the decrease in the number of Brn3a-positive cells induced by glutamate. In conclusion, NPY and NPY receptors can be considered potential targets to treat retinal degenerative diseases, such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Functional interaction between neuropeptide Y receptors and modulation of calcium channels in the rat hippocampus.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Feb;44(2):282-92. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00382-9. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12623227
-
Activation of Neuropeptide Y Receptors Modulates Retinal Ganglion Cell Physiology and Exerts Neuroprotective Actions In Vitro.ASN Neuro. 2015 Aug 26;7(4):1759091415598292. doi: 10.1177/1759091415598292. Print 2015 Jul-Aug. ASN Neuro. 2015. PMID: 26311075 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging novel roles of neuropeptide Y in the retina: from neuromodulation to neuroprotection.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24184719 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y inhibits [Ca2+]i changes in rat retinal neurons through NPY Y1, Y4, and Y5 receptors.J Neurochem. 2009 Jun;109(5):1508-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06079.x. Epub 2009 Apr 1. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19344373
-
Neuropeptide Y system in the retina: From localization to function.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015 Jul;47:19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25797468 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropeptide Y receptor activation preserves inner retinal integrity through PI3K/Akt signaling in a glaucoma mouse model.PNAS Nexus. 2024 Jul 26;3(8):pgae299. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae299. eCollection 2024 Aug. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 39114576 Free PMC article.
-
A Variant in Genes of the NPY System as Modifier Factor of Machado-Joseph Disease in the Chinese Population.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;14:822657. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.822657. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185528 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived β-hexosaminidase is essential for neuronal health and lysosome function: implications for Sandhoff disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 22:2024.10.21.619538. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.21.619538. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39484433 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Neuropeptide Y on Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells in Glutamate Excitotoxicity and ER Stress Conditions.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3665. doi: 10.3390/cells11223665. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429093 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y protects kidney against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by regulating p53-dependent apoptosis pathway.BMB Rep. 2016 May;49(5):288-92. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.5.231. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 26728272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dumont Y, Martel JC, Fournier A, St-Pierre S, Quirion R. Neuropeptide Y and neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes in brain and peripheral tissues. Prog Neurobiol. 1992;38:125–167. - PubMed
-
- Silva AP, Xapelli S, Grouzmann E, Cavadas C. The putative neuroprotective role of neuropeptide Y in the central nervous system. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2005;4:331–347. - PubMed
-
- Tatemoto K, Carlquist M, Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y—a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982;296:659–660. - PubMed
-
- Michel MC. Receptors for neuropeptide Y: multiple subtypes and multiple second messengers. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991;12:389–394. - PubMed
-
- Silva AP, Cavadas C, Grouzmann E. Neuropeptide Y and its receptors as potential therapeutic drug targets. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;326:3–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

