Plasma-assisted heparin conjugation on electrospun poly(L-lactide) fibrous scaffolds
- PMID: 23681664
- PMCID: PMC4894007
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34802
Plasma-assisted heparin conjugation on electrospun poly(L-lactide) fibrous scaffolds
Abstract
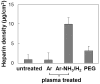
Heparin conjugation on poly(L-lactide) fibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning was accomplished by surface functionalization with amine (-NH2) groups using a sequential treatment with Ar-NH3 and H2 plasmas. The density of the incorporated -NH2 groups was determined by combining a chemical derivatization method with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The time of Ar-NH3 plasma treatment significantly affected the N/C, -NH2 /N, and -NH2 /C fractions, whereas the plasma power, Ar-NH3 gas composition, and time of H2 plasma treatment only influenced the -NH2 /N and -NH2 /C fractions. Scaffold surface functionalization by -NH2 groups significantly increased the amount of covalently bonded heparin compared to a hydrolysis method. The function of immobilized heparin was confirmed by the decrease of platelet attachment during the exposure of the scaffolds to blood from Sprague-Dawley rats. In vitro experiments with bovine aorta endothelial cells demonstrated that heparin conjugation enhanced cell infiltration through the fibrous scaffolds, regardless of the amount of covalently immobilized heparin.
Keywords: amine groups; conjugation; endothelial cells; heparin; infiltration; plasma treatment; platelets; surface functionalization.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
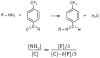



Similar articles
-
Plasma surface chemical treatment of electrospun poly(L-lactide) microfibrous scaffolds for enhanced cell adhesion, growth, and infiltration.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013 May;19(9-10):1188-98. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2011.0725. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013. PMID: 23281641 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of plasma and chemical modifications of poly-L-lactide-co-caprolactone scaffolds for heparin conjugation.Biomed Mater. 2017 Oct 5;12(6):065004. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/aa81aa. Biomed Mater. 2017. PMID: 28980527
-
Covalent immobilization of stem cell inducing/recruiting factor and heparin on cell-free small-diameter vascular graft for accelerated in situ tissue regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016 Jun;104(6):1352-71. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35666. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016. PMID: 26822178
-
[Studies on poly-D, L-lactide acid scaffolds modified by conjugation of bioactive peptides via ammonia plasma treatment].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;24(11):1376-85. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21226366 Chinese.
-
Controlled heparin conjugation on electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin fibers for morphology-dependent protein delivery and enhanced cellular affinity.Acta Biomater. 2012 Jul;8(7):2549-58. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.03.030. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Acta Biomater. 2012. PMID: 22465575
Cited by
-
Improved Osteogenesis of Selective-Laser-Melted Titanium Alloy by Coating Strontium-Doped Phosphate With High-Efficiency Air-Plasma Treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 May 12;8:367. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32478042 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and strategies for in situ endothelialization and long-term lumen patency of vascular grafts.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 5;6(6):1791-1809. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.11.028. eCollection 2021 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33336112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yoo HS, Kim TG, Park TG. Surface-functionalized electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:1033–1042. - PubMed
-
- He W, Yong T, Teo WE, Ma Z, Ramakrishna S. Fabrication and endothelialization of collagen-blended biodegradable polymer nanofibers: potential vascular graft for blood vessel tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:1574–1588. - PubMed
-
- Luong-Van E, Grøndahl L, Chua KN, Leong KW, Nurcombe V, Cool SM. Controlled release of heparin from poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun fibers. Biomaterials. 2006;27:2042–2050. - PubMed
-
- Koh HS, Yong T, Chan CK, Ramakrishna S. Enhancement of neurite outgrowth using nano-structured scaffolds coupled with laminin. Biomaterials. 2008;29:3574–3582. - PubMed
-
- He W, Ma ZW, Yong T, Teo WE, Ramakrishna S. Fabrication of collagen-coated biodegradable polymer nanofiber mesh and its potential for endothelial cells growth. Biomaterials. 2005;26:7606–7615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

