Staufen-mediated mRNA decay
- PMID: 23681777
- PMCID: PMC3711692
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1168
Staufen-mediated mRNA decay
Abstract
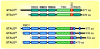
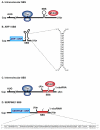
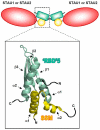
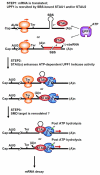
Staufen1 (STAU1)-mediated mRNA decay (SMD) is an mRNA degradation process in mammalian cells that is mediated by the binding of STAU1 to a STAU1-binding site (SBS) within the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of target mRNAs. During SMD, STAU1, a double-stranded (ds) RNA-binding protein, recognizes dsRNA structures formed either by intramolecular base pairing of 3'-UTR sequences or by intermolecular base pairing of 3'-UTR sequences with a long-noncoding RNA (lncRNA) via partially complementary Alu elements. Recently, STAU2, a paralog of STAU1, has also been reported to mediate SMD. Both STAU1 and STAU2 interact directly with the ATP-dependent RNA helicase UPF1, a key SMD factor, enhancing its helicase activity to promote effective SMD. Moreover, STAU1 and STAU2 form homodimeric and heterodimeric interactions via domain-swapping. Because both SMD and the mechanistically related nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) employ UPF1; SMD and NMD are competitive pathways. Competition contributes to cellular differentiation processes, such as myogenesis and adipogenesis, placing SMD at the heart of various physiologically important mechanisms.
Copyright © 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Staufen2 functions in Staufen1-mediated mRNA decay by binding to itself and its paralog and promoting UPF1 helicase but not ATPase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 8;110(2):405-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213508110. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23263869 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA-mRNA duplexes that autoelicit Staufen1-mediated mRNA decay.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1214-20. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2664. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24056942 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs via Alu elements.Nature. 2011 Feb 10;470(7333):284-8. doi: 10.1038/nature09701. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21307942 Free PMC article.
-
Up-frameshift protein 1 (UPF1): multitalented entertainer in RNA decay.Drug Discov Ther. 2012 Apr;6(2):55-61. Drug Discov Ther. 2012. PMID: 22622014 Review.
-
The multifunctional RNA-binding protein Staufen1: an emerging regulator of oncogenesis through its various roles in key cellular events.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7145-7160. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03965-w. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34633481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of APP interaction proteins by DUALmembrane yeast two-hybrid system.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):2802-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045787 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor interacts with PNRC2 in a ligand-dependent manner to recruit UPF1 for rapid mRNA degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 31;112(13):E1540-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409612112. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25775514 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding FMRP and Staufen sequentially regulate the Coracle scaffold to control synaptic glutamate receptor and bouton development.Development. 2022 May 1;149(9):dev200045. doi: 10.1242/dev.200045. Epub 2022 May 3. Development. 2022. PMID: 35394012 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on Translation Initiation of the HIV-1 mRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 28;20(1):101. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010101. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30597859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Variations of 3'UTR Length Reprogram the mRNA Regulatory Landscape.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 28;9(11):1560. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111560. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmid M, Jensen TH. Nuclear quality control of RNA polymerase II transcripts. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010;1:474–485. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Wilkinson MF. Regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012;3:807–828. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino S. Mechanism of the initiation of mRNA decay: role of eRF3 family G proteins. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012;3:743–757. - PubMed
-
- Harigaya Y, Parker R. No-go decay: a quality control mechanism for RNA in translation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010;1:132–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

